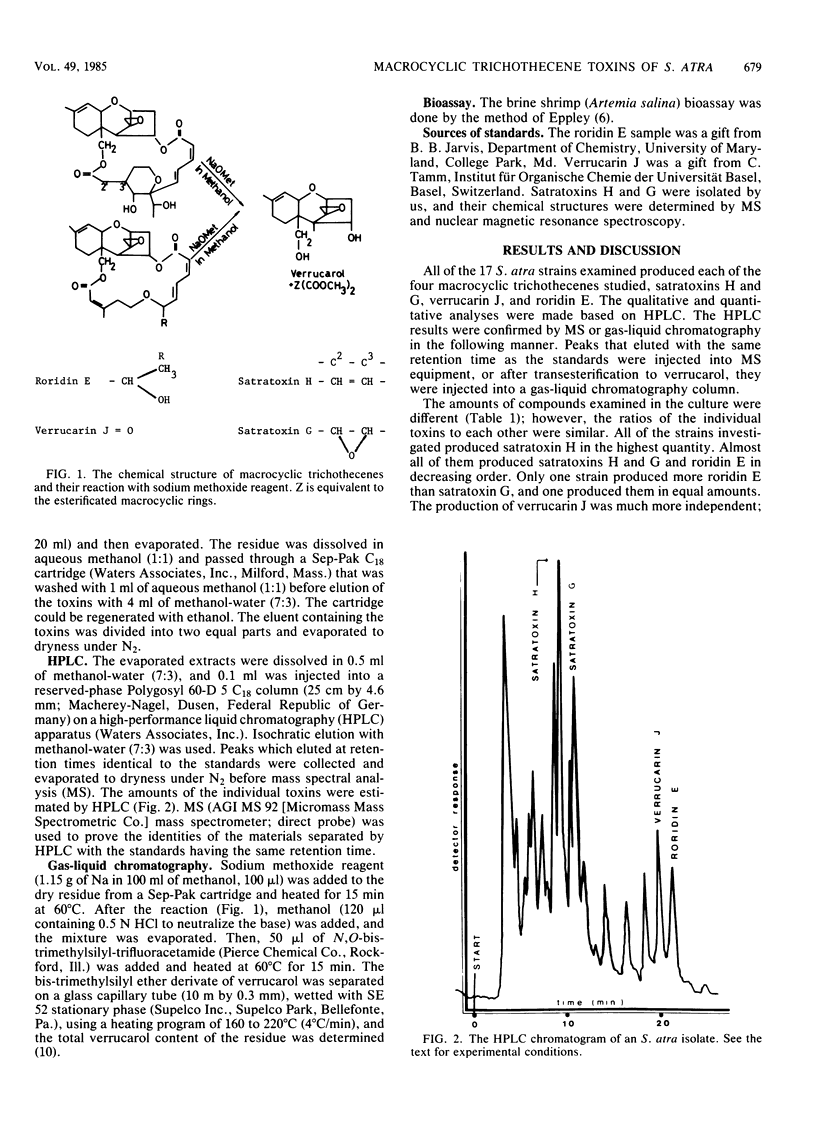
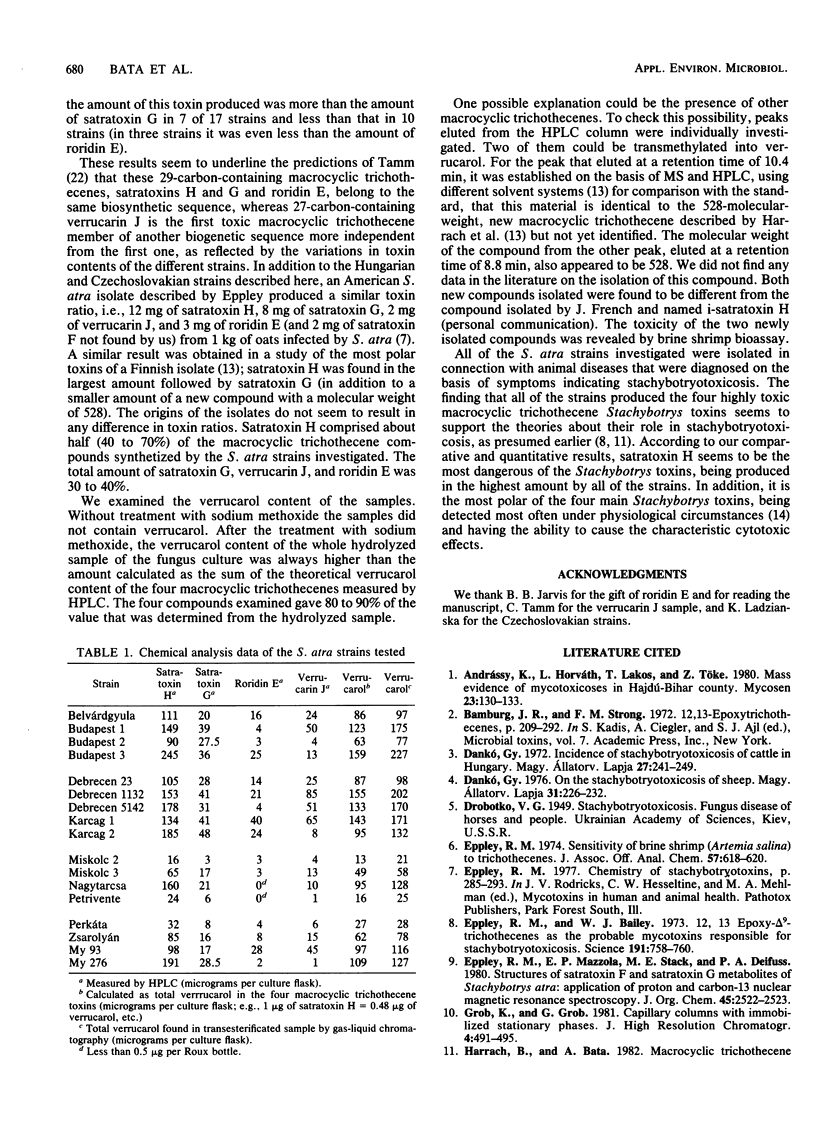
Abstract
A total of 17 strains of Stachybotrys atra isolated in Hungary and Czechoslovakia were cultured on Sabouraud agar, and the toxins produced by them were chemically analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography, high-pressure liquid chromatography, and mass spectroscopy. Furthermore, brine shrimp (Artemia salina) bioassay was used for the determination of toxicity of the compounds examined. Macrocyclic trichothecenes (satratoxins H and G, roridin E, and verrucarin J as well as two other unidentified macrocyclic trichothecenes) were found in all of the cultures tested. The identities of satratoxins H and G, roridin E, and verrucarin J were qualitatively determined by high-pressure liquid chromatography and gas-liquid chromatography. The ratio of satratoxins H and G and roridin E was found to be similar in each of the strains tested, but the amount of verrucarin J found was different in each of them. One of the unidentified macrocyclic trichothecenes was equivalent to the compound isolated by Harrach et al. (Harrach et al., Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 41:1428-1433, 1981). The other one proved to be a newly isolated macrocyclic trichothecene toxin. Stachybotryotoxicosis, one of the oldest mycotoxicoses known, and a serious problem in Middle Europe (Gy. Danko, Magy. Allatorv. Lapja 31:226-232, 1976), is believed to be caused by macrocyclic trichothecene toxins produced by Stachybotrys atra (R. M. Eppley, in Rodricks et al., ed., Mycotoxins in Human and Animal Health, p. 285-293, 1977). Forty years ago, the death of animals in the Soviet Union was associated with this fungus (C. U. Ruhliada, in Proceedings of the All-Union Sci. and Tech. Conf., p. 47-51, 1980).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrássy K., Horváth I., Lakos T., Töke Z. Massenhaftes Auftreten von Mykotoxikosen im Komitat Hajdu-Bihar. Mykosen. 1980 Mar;23(3):130–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppley R. M., Bailey W. J. 12,13-Epoxy-delta 9-trichothecenes as the probable mycotoxins responsible for stachybotryotoxicosis. Science. 1973 Aug 24;181(4101):758–760. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4101.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppley R. M. Sensitivity of brine shrimp (Artemia salina) to trichothecenes. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1974 May;57(3):618–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrach B., Bata A., Bajmócy E., Benko M. Isolation of satratoxins from the bedding straw of a sheep flock with fatal stachybotryotoxicosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1419–1422. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1419-1422.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrach B., Mirocha C. J., Pathre S. V., Palyusik M. Macrocyclic trichothecene toxins produced by a strain of Stachybotrys atra from Hungary. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1428–1432. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1428-1432.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrach B., Nummi M., Niku-Paavola M. L., Mirocha C. J., Palyusik M. Identification of "water-soluble" toxins produced by a Stachybotrys atra strain from Finland. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):494–495. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.494-495.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bars J., Gérard J. P., Michel C. Mise en évidence de la stachybotryotoxicose en France: un cas d'intoxication aiguë chez des daims. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1977;31(4-6):509–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nummi N., Niku-Paavola M. L. Water soluble toxins of Stachybotrys alternans. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1977;31(4-6):761–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. J., Marasas W. F., Dale Kuys J. C., Kriek N. P., Van Schalkwyk G. C. A field outbreak of suspected stachybotryotoxicosis in sheep. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 1979 Jun;50(2):73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


