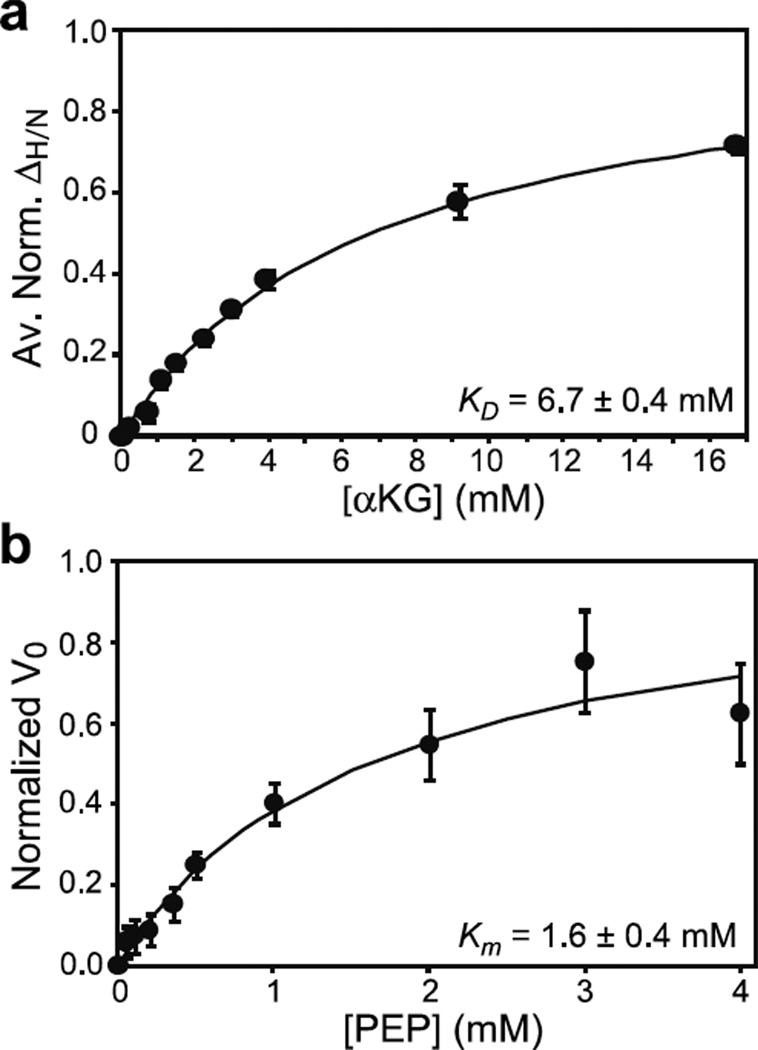
Figure 5. Effect of the active site R465A mutation on the binding of αKG and PEP to EIC.
(a) Binding of αKG to the R465A EIC mutant as monitored by chemical shift perturbation. Data for all residues showing ΔH/N > 0.1 ppm at 16 mM αKG were simultaneously fit (solid curve) using a one-site binding model (see Methods). In the figure, the ΔH/N were normalized with respect to the fitted ΔH/N at saturation and averaged over all the residues used in the fitting procedure. (b) Michaelis-Menten kinetics for the R465A EIC mutant with the substrate PEP in the absence of αKG. The error bars are set to one standard deviation.