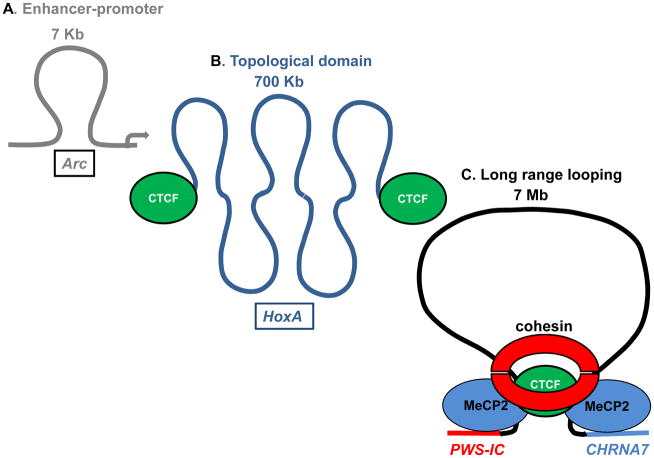
Figure 4. The epigenetic layer of chromatin looping is composed of at least three sublayers.
A. At the sub-layer of specific transcription units, enhancers and other distal units make contact with gene promoters such as Arc, a neuronal factor required for the regulation of AMPA receptors, via kb scale chromatin loops. Pol II (red) is recruited by enhancers where transcription initiates before transfer by looping to the Arc promoter [68]. B. Chromatin domains up to 1 Mb organize chromosomes into a series of functional units in mammalian cells. The insulating factor CTCF (green) regulates formation and maintenance of this intermediate layer in the HoxA locus and other domains genome wide [96]. C. Long range, multi-megabase chromatin loop interactions regulate gene expression between distant loci above the domain layer. At this layer, the PWS-IC (red) contacts the locus encoding CHRNA7 (blue) via a 7 megabase looping interaction via MeCP2 and potentially CTCF (green) and cohesion (red) [98, 99]. This long-range interaction modulates expression of CHRNA7 and other neurologic genes in 15q11–13 [98].