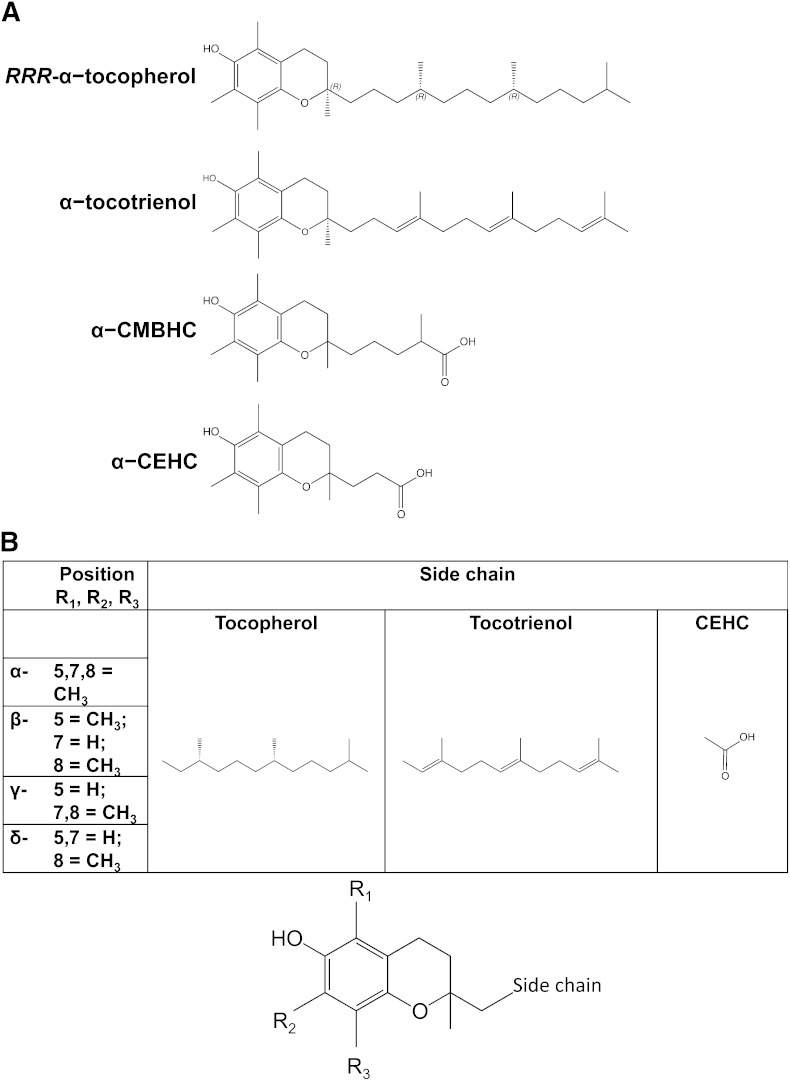
Fig. 1.
Vitamin E structures. (A) α-Tocopherol-related structures. From top to bottom: RRR-α-tocopherol with indicated stereochemistry on the side chain and at position 2, (R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-((4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)chroman-6-ol; α-tocotrienol, R-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-((3E,7E)-4,8,12-trimethyltrideca-3,7,11-trien-1-yl)chroman-6-ol; α-CMBHC: 2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2(2’-carboxymethylbutyl)-6-hydroxychroman, or 5-(6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-chroman-2-yl)-2-methyl-pentanoic acid; α-CEHC: 2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2(2’-carboxyethyl)-6-hydroxychroman, or 3-(6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchroman-2-yl)propanoic acid. (B) Various forms of vitamin E and its metabolites. The chromanol ring illustrated at the bottom indicates the position of the substituents at positions 5, 7, and 8 and the side-chain location. The table indicates the various substituents for each α, β, γ, and δ, as well as the side chains for tocopherols, tocotrienols, and CEHCs.