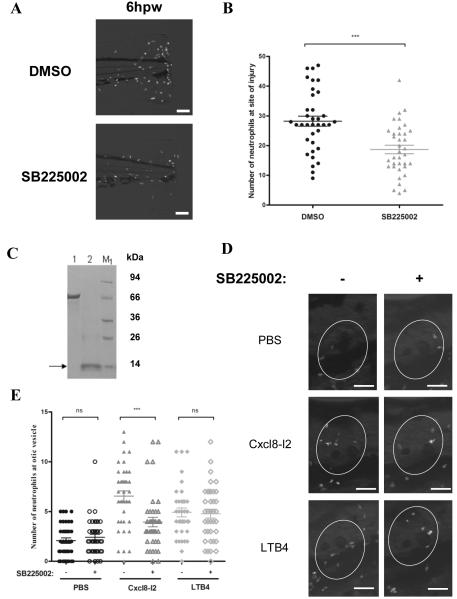
Figure 7.
Pharmacological inhibition of Cxcr2 impaired neutrophil recruitment. (A) Representative wide field fluorescence microscope micrographs of 3 dpf Tg(mpx:gfp)i114 control and morphant larvae, pre-treated or not with 5 μM SB225002 followed by tail fin wounding. Scale bar=100 μm. (B) Counts of fluorescent neutrophils at the wound were made at 6 hpw. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n=25 performed as 3 independent experiments). P values were calculated using two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, ** P<0.01. (C) SDS-Page analysis of Cxcl8-l2 recombinant protein. Lane 1: BSA (2μg), lane 2: Cxcl8-l2 (2μg). (D) Representative wide field fluorescence microscope micrographs of 3 dpf Tg(mpx:gfp)i114 pre-treated with 5 μM SB225002 followed by otic vesicle injection of PBS, 30 μM Cxcl8-l2 and /or 30 nM LTB4. Images were taken at 1 hpi. Scale bar=100μm. (E) Counts of fluorescent neutrophils recruited to the ear (encircled) were made 1 hpi. Data indicate means ± SEM (n=32 performed as 3 independent experiments). P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni multiple comparison, ***P<0.001.