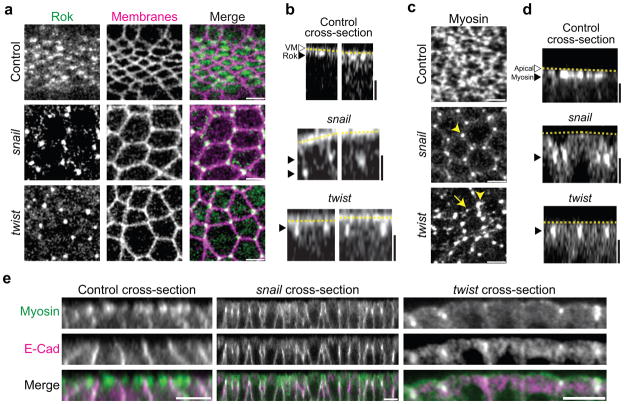
Figure 7.
Twist is required for medioapical radial cell polarity of Rok and Myo-II.
(a) twist and snail mutants result in an inversion of Rok RCP. Images are apical surface projections from live control, snail, or twist mutant embryos expressing GFP::Rok(K116A) and Gap43::ChFP. Rok abnormally localizes to junctions at three-way vertices in snail and twist mutants. (b) Rok localizes subapically in snail mutants, similar to position of the junctions, while Rok is present apically in control (twist/+) or twist mutants. Cross-section views of embryos from a. Dotted lines indicate the vitelline membrane (VM, white arrowhead). (c) Myo-II localization in snail and twist mutants mirrors Rok localization. Images are from live, control and snail or twist mutant embryos expressing Myo::GFP. Control embryos (twist/+) possess dense medioapical Myo-II meshwork, whereas Myo-II localizes to cell vertices in both snail and twist mutants (arrowheads). Myo-II transiently appears in medioapical foci in twist mutants during constriction pulses (arrow). (d) The apical-basal position of Myo-II mirrors the position of Rok. Images are cross-section views of embryos from c. Myo-II remains subapical in snail mutants, but localizes apically in control and twist mutants. (e) Apical-basal position of Myo-II corresponds to position of adherens junctions. Myo-II localizes to subapical adherens junctions in snail mutants and to apical junctions in twist embryos. Images are cross-sections of fixed embryos expressing Myo::GFP and stained for E-Cadherin. Scale bars are 5μm.