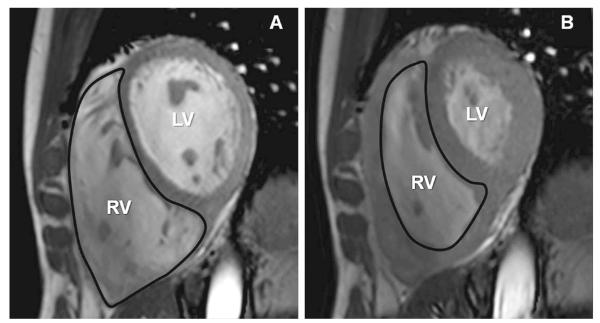
Figure 4.
End-diastolic (A) and end-systolic (B) cine short-axis images from a patient with PH. Hypertrophy and dilation of the right ventricle in PH is the result of the increased pressure placed on the ventricle to maintain blood flow in the face of high vascular resistance. Increased mass in the right ventricle leads to a higher oxygen requirement. Without the appropriate blood supply, this imbalance can lead to myocardial hypoxia and a variety of cellular abnormalities. Adapted with permission from 82.