Figure 2.
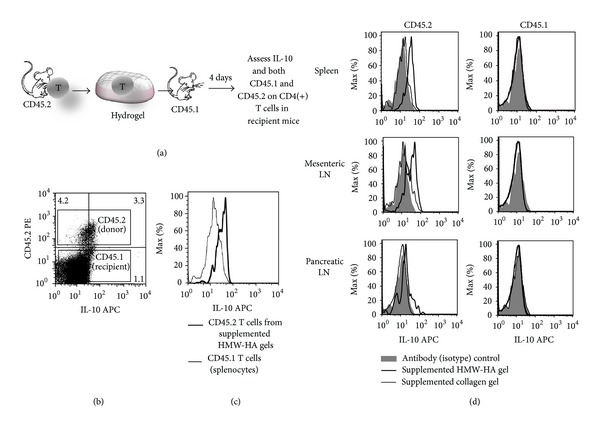
Supplemented HA hydrogels induce IL-10 in vivo. (a) Diagram of the experiment. Supplemented HA hydrogels, or control collagen hydrogels lacking HA, were populated with 3 × 106 CD4(+)/GFP-FoxP3(–)/CD45.2 donor cells and injected into the peritoneal cavities of CD45.1 recipient mice. Four days after implantation, lymphoid tissues were harvested, processed, and stained for intracellular IL-10 and CD markers. (b) Gating indicates relative IL-10 expression by CD45.2 donor and CD45.1 host T cells. (c) IL-10 expression by CD45.2 donor T cells harvested from HA hydrogel residue removed from the peritoneal cavity is substantially greater than that of CD45.1 host T cells from the spleen. (d) IL-10 staining of CD3(+)/CD4(+) T cells harvested from the spleen and mesenteric/pancreatic lymph nodes (LN). The donor T cells from mice that received the supplemented HA hydrogels expressed higher levels of IL-10 than corresponding donor T cells from mice that received the control supplemented collagen hydrogels. Host T cells from these two groups of mice did not express IL-10 above levels of the nonspecific antibody (isotype) controls. In (c), and (d), data are representative of three experiments each.
