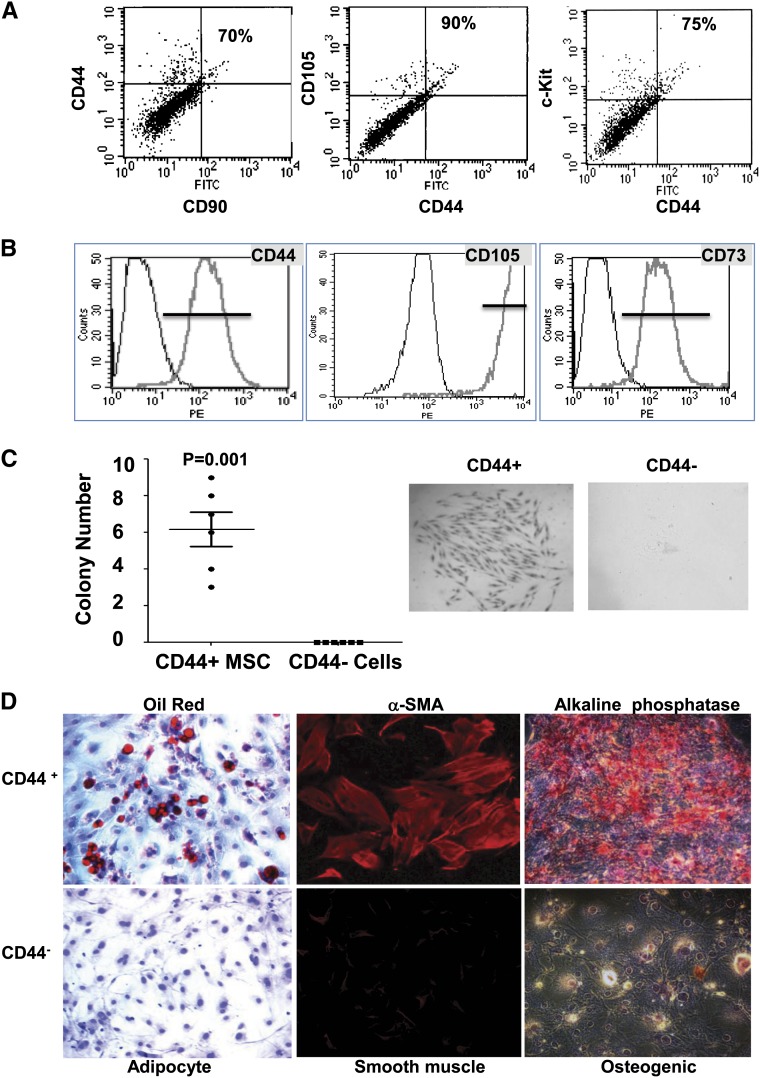
Figure 1.
CD44+ MSC-like cells can be isolated from the adult mouse kidney. (A) Cells were isolated by FACS from the renal cortex of 6- to 8-week-old male C57BL/6 mice and stained with typical adult tissue stem cell/progenitor cell markers (CD44, c-Kit, CD90, and CD105) to evaluate their expression. Representative data are presented, and percentages of double-positive cells versus total CD44+ cells are indicated. (B) Typical MSC surface markers expressed in isolated CD44+ cells after three to five passages in culture as analyzed by FACS. (C) Mouse renal CD44+ or CD44− cells were assayed for clonogenicity using the colony forming unit (CFU) assay. Left panel shows the quantification of CFU formation after 14 days in culture as measured by Giemsa staining and microscopy. Representative CFU images acquired by light microscopy (middle and right panels; original magnification, ×10). (D) Multilineage differentiation capacity of renal CD44+ cells. Renal CD44+ and CD44− cells were isolated and cultured for three to five passages before the induction of differentiation. Left panels: Images of cells cultured in adipogenic induction medium for 2 weeks, showing oil red–stained lipid droplets. Middle panels: Images of cells cultured in osteogenic induction medium for 3 weeks. Alkaline phosphatase staining (red). Right panels: Images of CD44+ and CD44− cells after 6 days of induction toward smooth muscle lineage. Expression of the SMC specific marker α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA) is shown in red. Original magnification, ×20.