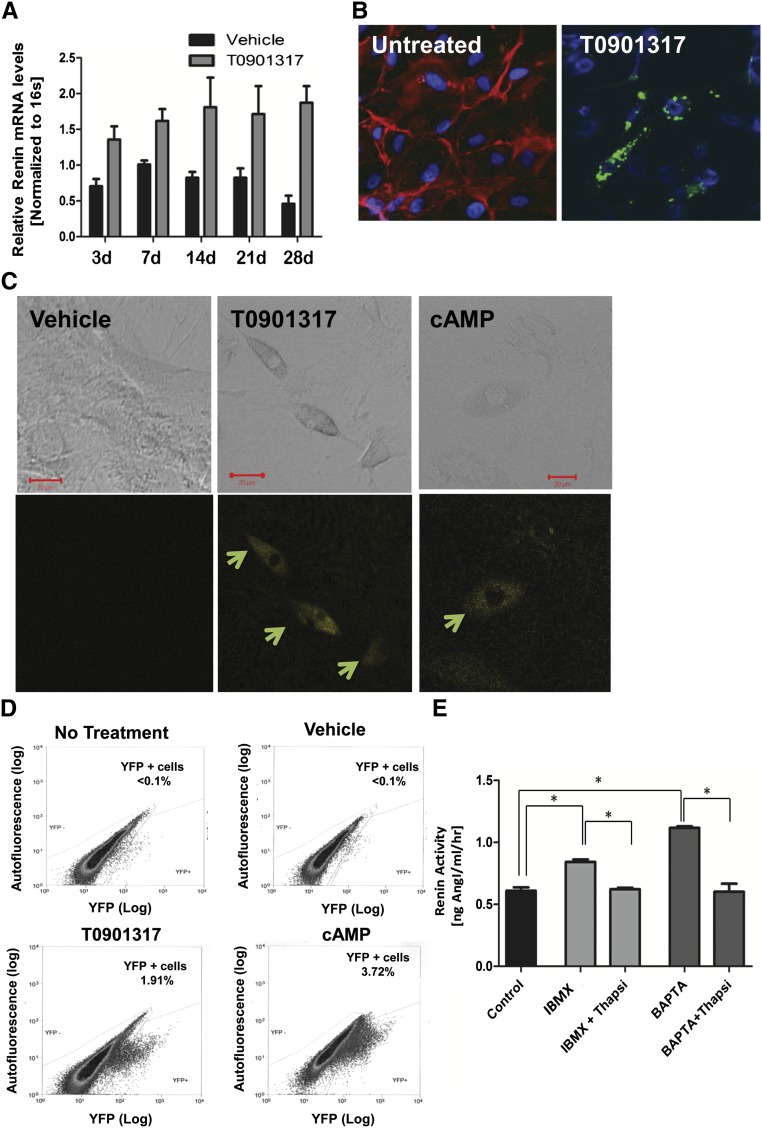
Figure 2.
Mouse renal CD44+ MSC-like cells can differentiate into renin producing JG-like cells in vitro. Renal CD44+ and CD44− cells were isolated from adult male mice and cultured in growth medium for three to five passages before use. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of CD44+ cells treated with T0901317 (1 µM) (gray bars) or vehicle (black bars), n=3 in each group. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. P=.0004 for treatment (two-way ANOVA). (B) High magnification (40×) confocal images showing double-staining for CD44 (red) and renin (green) in renal CD44+ cells treated with T0901317 for 4 weeks. Note the granular pattern, typical of renin expression. CD44 expression (red) decreased or disappeared during the differentiation process. Untreated; differentiation day 0; n=5. (C) Representative confocal images (32×; scale bar, 20 µm) of C57BL/6 Ren1C YFP mouse renal MSC CD44+ cells treated for 21 days with cAMP (1 mM), T0901317 (LXRα ligand, 1 μM), or DMSO (vehicle). YFP (yellow) is used as a surrogate marker for renin expression (arrows). (D) FACS analysis of renal CD44+ cells treated with DMSO (vehicle), T0901317 (LXRα synthetic ligand, 1 µM), or cAMP (1 mM) or no treatment for 21 days. Representative data are shown, n=7. (E) Renin activity in the medium of the differentiated cells induced by T0901317 for 2 weeks, followed by the stimulations with IBMX, or the [Ca2+]i chelator BAPTA-AM, with or without thapsigargin (thapsi). Data are presented as the mean + SEM, n=8. *P<0.05 for all group comparisons indicated (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used).