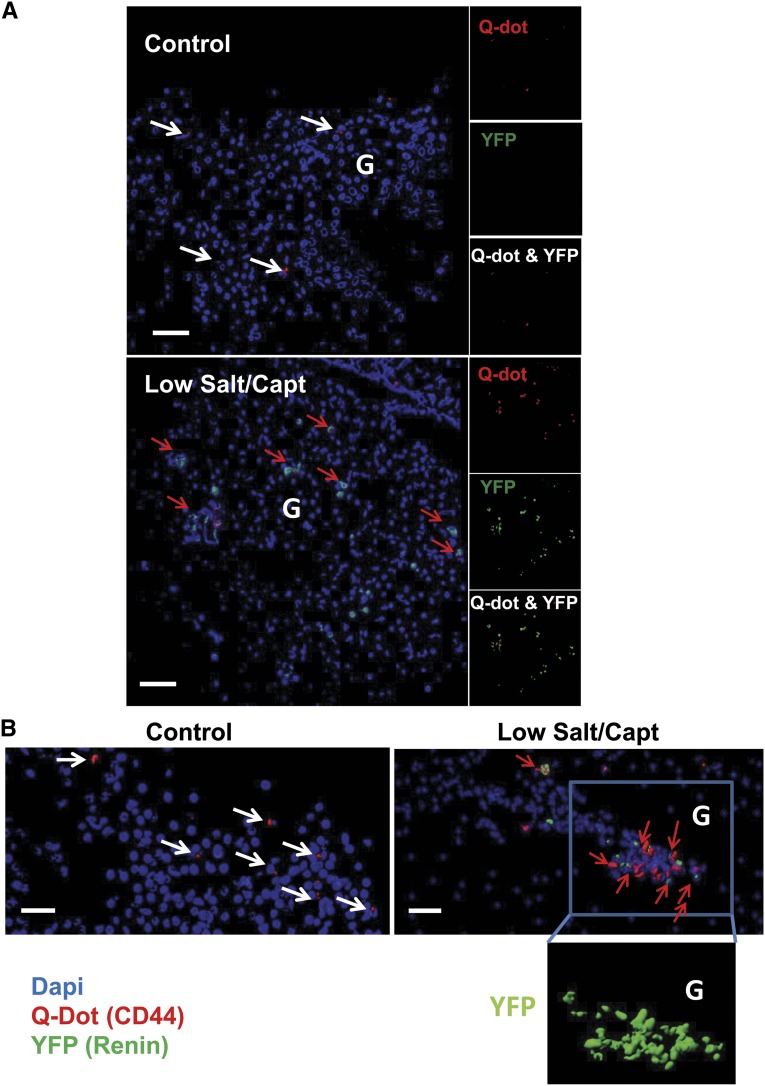
Figure 3.
Mouse renal CD44+ MSC-like cells can differentiate into renin producing JG-like cells in vivo. Q Dot (red) prelabeled mouse renal CD44+ cells from C57BL/6 Ren1c YFP transgenic mice injected into renal artery of wild type mice. Mice were kept on normal chow diet or low-salt diet and captopril treatment as described in the Material and Methods section. (A) Isosurface rendering of representative multiphoton microscopy images (25×) from the kidneys after three-dimensional reconstruction using Imaris software showing nuclei (blue), and YFP (shown as green) and Q Dot (red) in the kidney of normal chow diet control mice and low-salt/captopril (Capt)–treated animals; scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Isosurface rendering of representative multiphoton microscopy images (25×) in low-salt/captopril–treated mice. White arrows point to Q dot–positive cells and red arrows point cells double positive for Q dot and YFP. Boxed area highlights the presence of YFP (renin)-expressing transplanted Ren1c YFP CD44+ cells in the glomerulus (G) area. Note that the presence of YFP could be attributed only to the injected Ren1c YFP CD44+ MSCs; Q dot labeling serves as a secondary control for the engraftment of injected cells.