Figure 1.
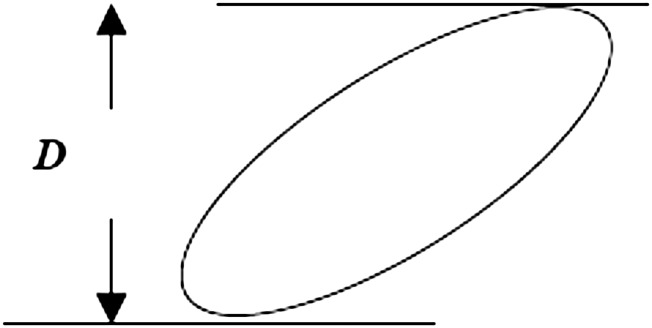
The caliper diameter is the distance D between parallel tangent lines (just touching the object) in any given direction. Note that D will differ depending on the orientation of the tangent lines. The probability of hitting a particle with a single section through a reference space is proportional not only to the density of particles in the space, but to the size of the particle and the thickness of the section. The particle size is quantified by the mean caliper diameter, 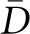 , which is the average—over all particle orientations—of the maximum extent of the particle between two parallel planes (calipers).
, which is the average—over all particle orientations—of the maximum extent of the particle between two parallel planes (calipers).
