Fig. 27.3.
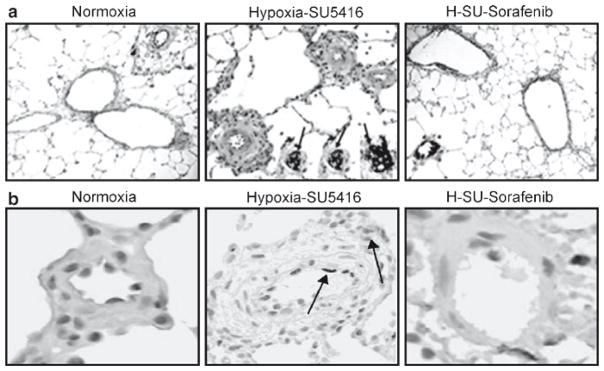
Effect of sorafenib on the development of PH histopathology. Representative images for each group (hematoxylin and eosin staining) with inset (anti-vWF staining) demonstrate that compared to normoxic rats (a), rats exposed to hypoxia/SU5416 showed marked vascular remodeling with medial wall thickening, endothelial cell hyperproliferation, and formation of plexiform lesions with exuberant vWF-positive endothelial cell proliferation (three representative inset arrows). Sorafenib completely prevented the chronic hypoxia-SU5416-induced vascular remodeling. Differences in the level of apoptosis detected by cleaved caspase 3 staining and the level of cell proliferation using Ki67 staining were quantified as brown IOD per 10 μM2 using ACIS. (b) Representative images for apoptosis from each condition. A stepwise increase in staining for apoptosis was demonstrated with hypoxia/SU5416 exposure compared to normoxia. Sorafenib produced dramatic inhibition of apoptosis compared to the hypoxia/SU5416 model, with less attenuation compared to hypoxia. #p < 0.05
