Figure 1.
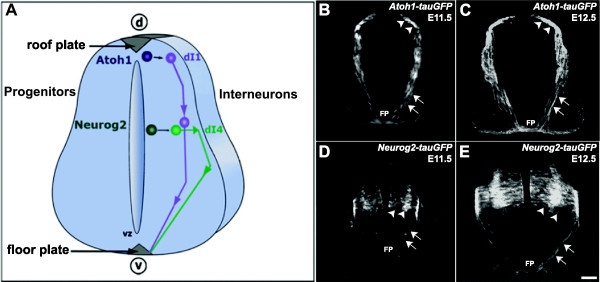
Atoh1-tauGFP and Neurog2-tauGFP transgenic mice direct GFP expression to distinct populations of spinal commissural neurons. (A) Schematic of the embryonic mouse spinal cord in transverse view. In the developing mouse spinal cord, Atoh1 or Neurog2 progenitors give rise to dI1 and dI4 dorsal interneurons, respectively, that both project axons towards the floor plate (FP) and across the ventral commissure (VC). (B, C) In transverse cryosections derived from E11.5 and E12.5 Atoh1-tauGFP mouse embryos, tauGFP expression is present on a subset of dorsal progenitors, as well as on the dI1 interneurons that they differentiate into and their axons. (D, E) Cryosections from E11.5 and E12.5 Neurog2-tauGFP mice have tau-GFP localized to a distinct, more ventrally located subset of progenitors (arrowheads), as well as the dI4 interneurons that they differentiate into and their axons. Note that the pre-crossing segments of the labeled dI1 axons in B and C, project along a more medial route to the FP relative to their dI4 counterparts, in D and E, which project to the FP along a lateral trajectory. In both Atoh1-tauGFP and Neurog2-tauGFP mice, GFP expression is associated with pre- (arrows mark these axonal segments as they project toward the ventral midline) and post-crossing (asterisks mark these axonal segments as they project in the longitudinal plane within the marginal zone) segments of commissural axons. Arrowheads indicate positions of dI1 and dI4 cell bodies. Scale bar in E, 100 μm for B-E.
