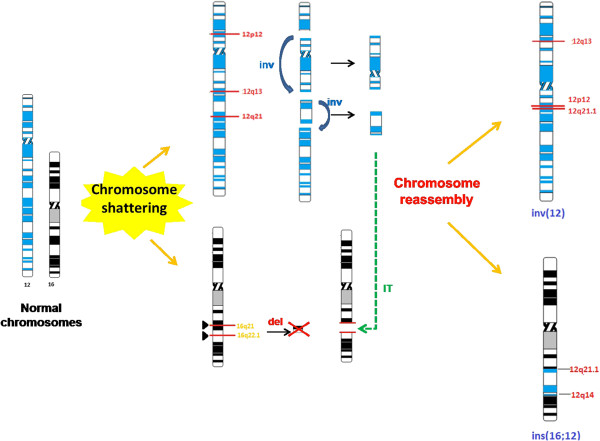
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of possible mechanisms cause of the complex chromosomal rearrangement in the proband. DNA double-strand breaks are formed as a result of "chromosome shattering" (triangles blacks) with the corresponding formation of chromosomal fragments that are rearranged through the phenomenon of "chromosome reassembly". The result is the formation of inversions (inv, blue arrows), deletions (the black arrow) and insertional translocation (IT, green dashed arrow) that originate the two derivative chromosomes: chromosome 12 with a pericentric inversion and deletion of 12q14q21.1 and chromosome 16 with the concomitant insertion of the 12q14q21.1 region with inverted sense in place of the 16q21-22.1 region that is deleted.