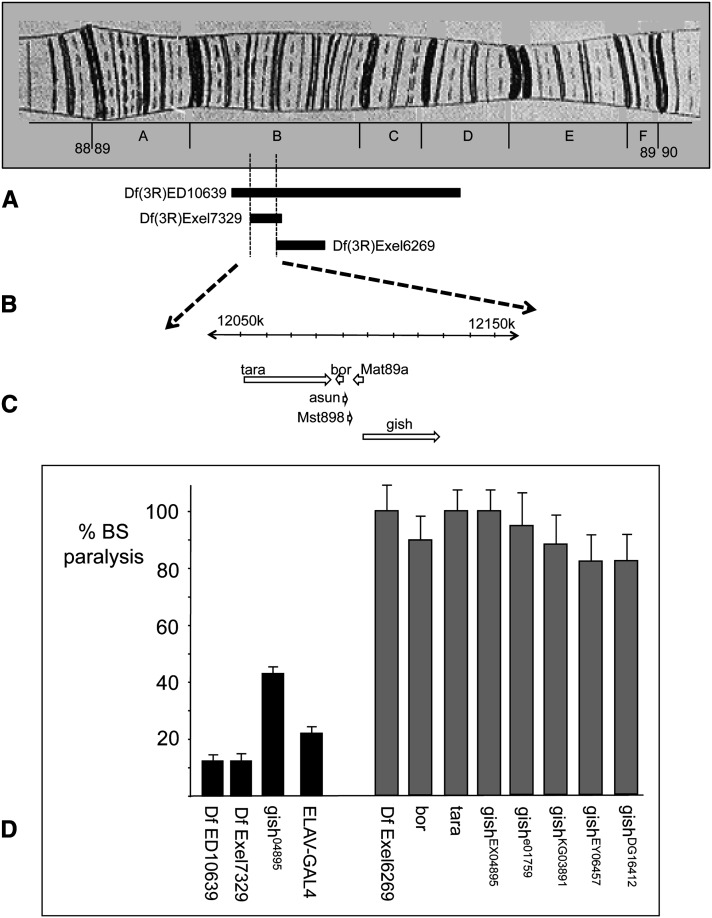
Figure 4.
Suppression of parabss1/+ BS paralytic phenotype by a heterozygous chromosomal segment deleted in 89B. (A) Depicted is polytene chromosome map of region 89 on 3R. (B) The segment deleted in Df(3R)ED10639 causes suppression of parabss1/+ BS paralysis, as described in the text. Also, Df(3R)Exel7329 causes suppression but Df(3R)Exel6269 does not. The breakpoints of these rearrangements delimit a small region (89B9 to 89B12) responsible for seizure suppression. (C) Six genes are contained in the 89B9 to 89B12 chromosomal segment including tara, bor, and gish. (D) BS paralytic phenotypes (% BS paralysis) of several genotypes in a parabss1/+ background, as described in the text. Genotypes showing BS suppression are depicted as black bars; gray bars are used in genotypes showing no suppression. In each case, the experimental genotype shown is normalized relative to sibling controls. Df ED10639 is the genotype parabss1/+; Df(3R) ED10639/+ showing 13% BS paralysis (87% suppression of BS phenotype). This indicates the apparent presence of a gene that acts as a haplo-seizure suppressor. Df Exel7329 is parabss1/+;Df(3R)Exel7329/+ showing 13% BS paralysis and providing one boundary for suppressor location at 89B9 based on inclusion within the deleted segment. Df Exel6269 is parabss1/+;Df(3R)Exel6269/+ showing 100% BS paralysis and providing a second boundary for suppressor location at 89B12 based its exclusion from the deletion. Flies that are parabss1/+;borc05496/+ and parabss1/+;tara1/+ (labeled bor and tara) show no suppression with 91% and 100% BS paralysis, respectively. Flies that are parabss1/+;gish04895/+ (labeled gish04895) show 43% BS paralysis, indicating suppression of the BS paralytic phenotype. Flies that are parabss1/+;gishEX04895/+ (labeled gishEX04895) are a line with a remobilized, precise excision of the gishEX04895 P-element; they show no suppression with 98% BS paralysis. Flies that are ELAV-Gal4C155 parabss1/+; UAS-gishRNAi/+ (labeled ELAV-GAL4) show 25% BS paralysis indicating suppression of the BS paralytic phenotype. Several gish alleles as heterozygotes show no suppression of parabss1/+ BS paralytic phenotypes. Thus, gishe01759/+, gishDG16412/+, gishKG03891/+, gishEY06457/+ heterozygous combinations in a parabss1/+ background show 95%, 88%, 84%, and 83% BS paralysis, respectively.