Figure 1. Localisation and sequence of the immunosuppressive (isu) domain of the TM protein of HERV-K (accession number Q69384).
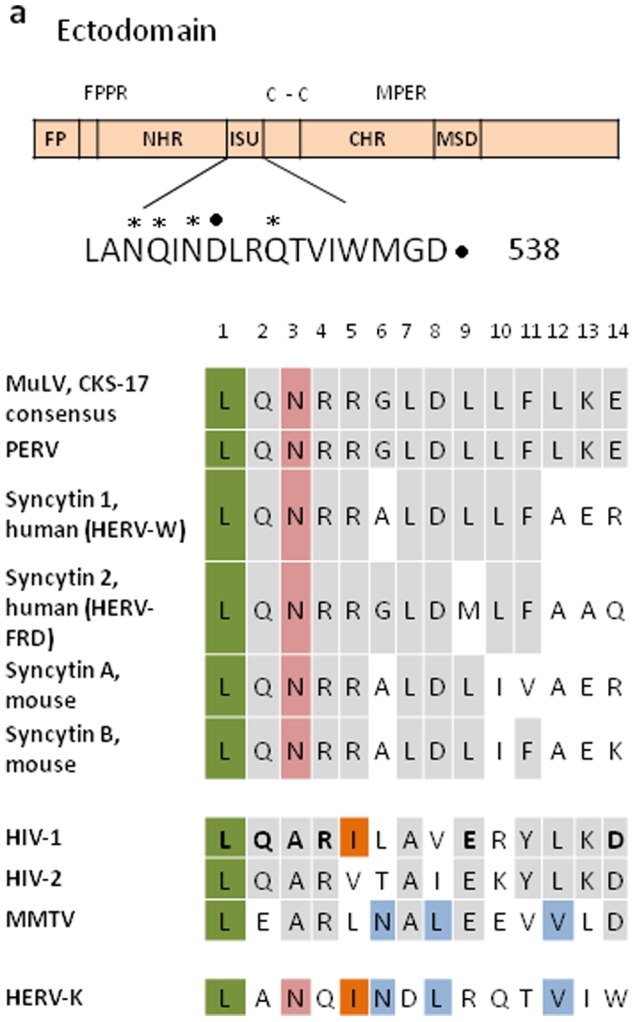
a, Functional domains of the TM protein: FP, fusion peptide; FPPR, fusion peptide proximal region; NHR, N-terminal helical region; ISU, isu domain; C-C, cystein-cystein loop; CHR, C-terminal helical region; MPER, membrane proximal external region; MSD, membrane spanning domain. In the amino acid sequence of the isu domain stars (*) indicate NH2 groups, points (.) mark COOH groups relevant for polymerisation. b, Sequence comparison of the core (1 corresponds to the amino acid 552, 14 to 535, acc. Nr. Q69384) of the immunosuppressive domain of different retroviruses (MuLV, murine leukaemia virus; CKS-17 consensus, consensus sequence of the gammaretroviruses PERV, porcine endogenous retrovirus; HERV-K, -W, -FRD; human endogenous retroviruses-K, -W, -FRD; HIV-1, -2, human immunodeficiency viruses - 1, -2¸ MMTV, mouse mammary tumour virus; HERV-K, human endogenous retrovirus-K). Amino acids identical to that in the first sequence of each group are indicated gray. In addition, amino acids present in all retroviruses are marked green, in all gammaretroviruses and HERV-K pink, in HIV-1 and HERV-K orange and in MMTV and HERV-K blue. In the sequence of HIV-1 the amino acids with high importance are shown in bold, mutation of these amino acids totally abrogated the activity to induce IL-10 [27].
