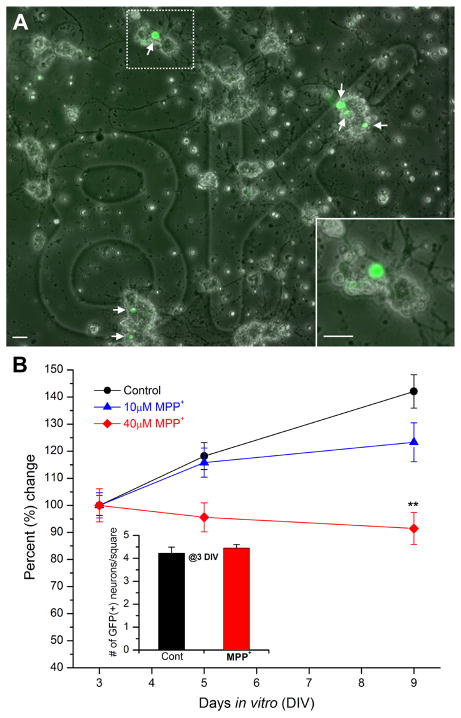
Figure 1. MPP+ reduces number of dopaminergic neurons in Drosophila primary culture.
(A) An overlapped image of bright-field and GFP signals in a marked square (8K in this case). Six GFP(+) dopaminergic (DA) neurons are indicated by arrows. Neuronal cultures were derived from a cross between TH-Gal4 and UAS-GFP lines (=TH-GFP). As shown previously (Park et al, 2007), these cultures were plated onto photoetched coverslips which allow for identifying a square containing GFP(+) neurons that can then be returned to at a later time. Scale bar = 20μm. Inset An enlarged view of the dotted square in (A). showing a GFP(+) neuron is in a neuronal cluster containing GFP(−) neurons. (B) A graph showing percent change in number of GFP(+) DA neurons in the absence and presence of MPP+. Number of GFP(+) neurons at 5 and 9 days in vitro (DIV) was normalized to that at 3 DIV. The control and MPP+ treated cultures have a similar number of GFP(+) DA neurons at 3DIV (Inset, see below). However, at 9 DIV, the number of GFP(+) neurons in the control dish has increased while the number has slightly decreased in the MPP+ treated cultures. Inset A graph showing number of GFP(+) neurons per each square averaged at 3 days in vitro (DIV). Coverslips were randomly split into three groups: control, 10μM MPP+ or 40μM MPP+. Control (n=110), 10μM MPP+ (n=55) & 40μM MPP+ (n=61) from total 6 separate experiments. Student t-test, *P<0.05 & **P<0.01.