Figure 2.
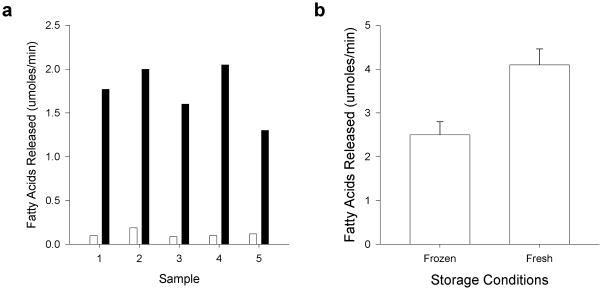
Activity of human milk lipases in the presence of bile salts and after freeze-thaw. (a) The release of fatty acids from human milk was measured in the pH-stat with and without a mixture of physiological bile salts as described in Methods. Frozen human milk was obtained from three separate donors. Sample 1 = donor 1; Sample 2 = donor 2; Samples 3, 4 and 5 = donor 3. Black bars, no bile salts; Grey bars, plus bile salts. The difference of the means of no bile salts and plus bile salts for all samples was significant, P<0.001. (b) The release of fatty acids from frozen milk stored less than one week and from fresh human milk. The milk was from donor 3. The assay was done with a mixture of physiological bile salts (4 mM) in the pH-stat as described in Methods. The difference between the means was significant, P = 0.001.
