Figure 3.
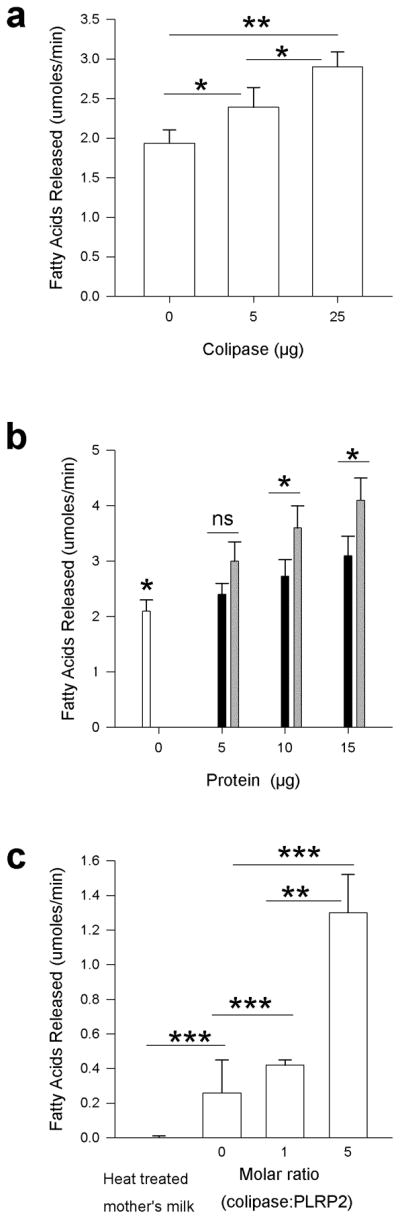
The influence of colipase and PLRP2 on lipolysis of human milk fats in the presence of bile salts. In each experiment activity was measured in the pH-stat in the presence of 4 mM bile salts as described in Methods. The P-value is given for the pair-wise comparisons between the different groups. (a) The release of fatty acids from frozen human milk after addition of various amounts of human colipase. *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01 (Student’s t-test). (b) Release of fatty acids from frozen human milk by the combination of PLRP2 and colipase at various concentrations. The amount of colipase or PLRP2 or both that was added to the incubation is indicated by the x-axis. White bar, human milk alone; Black bar, colipase alone; Gray bar, colipase and PLRP2; the same mass (μg) of colipase and PLRP2 were added as indicated. This resulted in a 5-fold molar ratio of colipase to PLRP2. *P≤0.05 (Student’s t-test). (c) Release of fatty acids from heat-treated human milk by 25 μg of human PLRP2 in the presence of a physiological mixture of bile salts (4 mM) and various concentrations of colipase. **P≤0.01; ***P≤0.001 (Student’s t-test).
