Fig. 6.
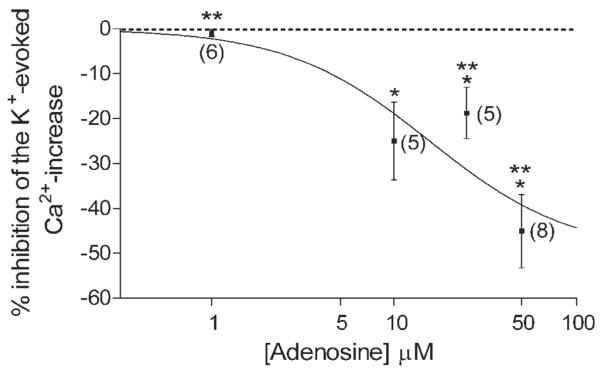
Concentration-dependent inhibition of the K+-evoked [Ca2+]i increase in isolated cones by adenosine. This graph summarizes the inhibition of the K+-evoked Ca2+ increase in the terminals of all cones tested to different concentrations of adenosine. Fluo-4-loaded cones were stimulated with elevated [K+]o in the presence of different concentrations of adenosine (1–50 μM). Inhibition of K+-evoked change produced by adenosine was normalized to the average of the initial control and the subsequent recovery following the test solution. Each point represents the mean ± SE. Number of experiments is shown in parentheses. ⋆P < 0.05 compared with control. Adenosine concentrations: 1 μM: −1.0% ± 0.8%, n = 6, P = 0.0908; 10 μM: −25.0% ± 8.7%, n = 5, P = 0.0168, 25 μM: −18.8% ± 5.7%, n = 5, P = 0.0299, 50 μM: −45.1% ± 8.2%, n = 8, P = 0.0009. ⋆⋆P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA using Neuman-Keuls post hoc multiple-comparisons test shows that the inhibition of the K+-evoked Ca2+ increase by adenosine in cones at 1 μM, 25 μM, and 50 μM are significantly different demonstrating a concentration-dependent effect of adenosine on cones.
