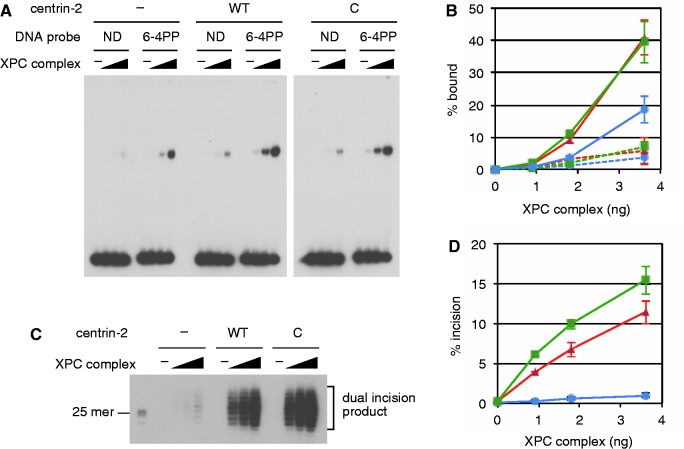
Figure 4.
The C domain of centrin-2 is sufficient to enhance both damaged DNA binding and NER dual incision activities of XPC. (A) EMSA was carried out, in which the DNA substrate (0.35 nM) with or without a single site-specific 6-4PP was included. Three different concentrations of XPC/RAD23B, with or without centrin-2 (WT or C), were used. (B) Percentage of the shifted DNA probe was calculated from each lane in panel A and plotted as a graph. Solid and broken lines represent the 6-4PP-containing and non-damaged (ND) DNA probes, respectively. Blue: no centrin-2, red: WT centrin-2, green: the C domain of centrin-2. (C) In vitro NER dual incision assays were carried out with purified NER proteins and internally 32P-labeled DNA substrate including a single 6-4 PP. Only part of the autoradiography containing dual incision products is shown. Exactly the same amounts of the XPC complex as used in panel A were included in the reactions. (D) Percentage of the incised DNA substrate was calculated from each lane in panel (C) and plotted as a graph. Blue: no centrin-2, red: WT centrin-2, green: the C domain of centrin-2. For panels (B) and (D), the mean values and standard errors were calculated from two independent experiments, respectively.