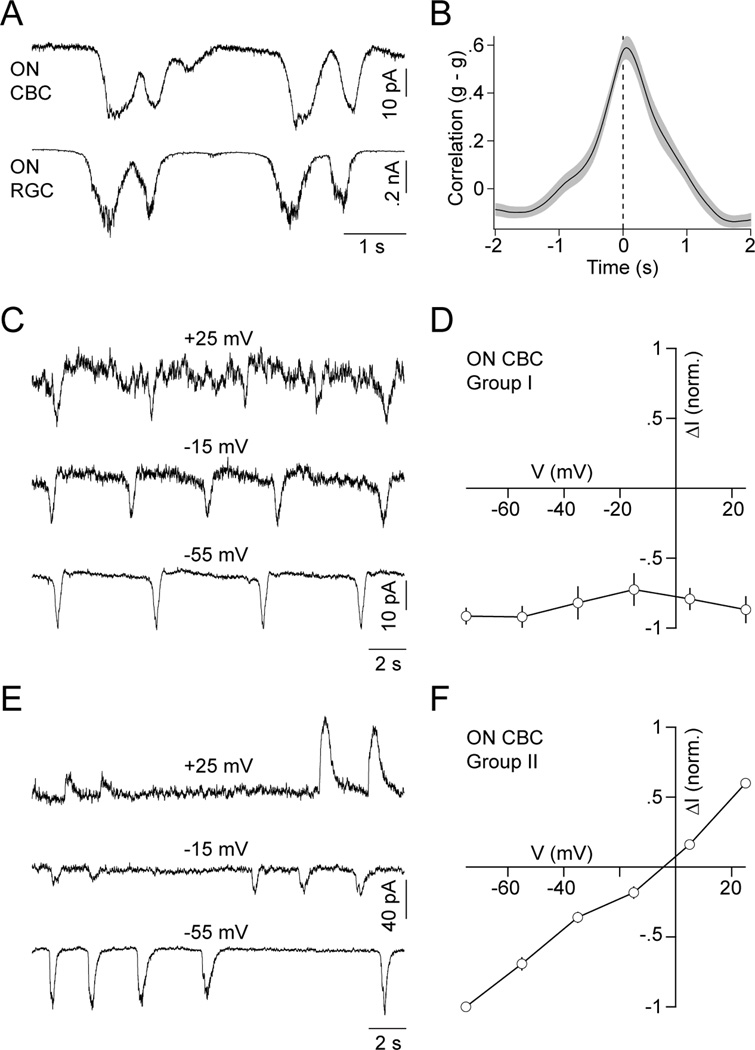
Figure 6. ON CBCs receive excitatory input during waves via cation-nonselctive conductances and gap junctions.
(A) Simultaneous recording of EPSCs of an ON CBC and ON RGC during stage III waves. (B) Crosscorrelation (mean ± SEM, n = 8) of excitatory synaptic conductances (g) of ON CBCs and ON RGCs. (C, E) Voltage-clamp traces of a representative group I (C) and II (E) ON CBC in the presence of strychnine (500 nM), gabazine (5 µM) and TPMPA (50 µM) at a series of holding potentials. (D, F) Normalized I-V relationship (mean ± SEM) of wave-associated input currents to group I (D, n = 3) and II (F, n = 3) ON CBCs during blockade of inhibitory synaptic transmission.