Fig. 1.
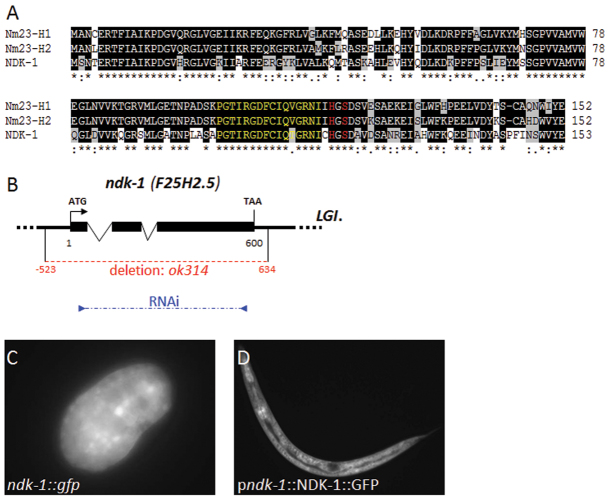
C. elegans ndk-1 is an essential gene. (A) Sequence alignment of human NM23-H1 (NME1), NM23-H2 (NME2) and C. elegans NDK-1 (F25H2.5) proteins. Identical and similar residues are highlighted with black and gray shading, respectively. NDK-1 shows 85% overall similarity to both NM23-H1 and -H2 isoforms. Amino acids His118 and Ser120 (red), which are essential for kinase activity and NDPK multimer formation, respectively, are conserved in these proteins. A 16 amino acid stretch N-terminal to the catalytic site at His118 (yellow) is also highly conserved. (B) Genomic structure of the ndk-1 gene. Sequencing of the ndk-1 full-length cDNA clone yk1105 confirmed the exon-intron structure predicted by WormBase. The dotted red line shows the position of the ok314 deletion, which includes the complete ORF of ndk-1, a 523 bp 5′ regulatory region and 34 bp of the 3′UTR. The position of primers used for generating the ndk-1 RNAi clone is indicated in blue. (C) Ubiquitous expression of a transcriptional ndk-1::gfp reporter in a comma stage C. elegans embryo. (D) Expression of a functional translational fusion NDK-1::GFP reporter in an L2 stage larva.