Fig. 4.
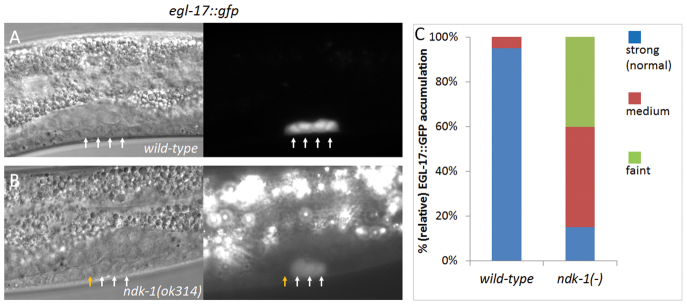
EGL-17::GFP expression is much reduced in P6p.xx cells of ndk-1(-) mutants. The accumulation of EGL-17/FGF, a marker for Ras-dependent vulval fate induction (egl-17 is an EGFR/Ras/MAPK signaling target), in the P6.p granddaughters, in which signaling actually occurs. (A) EGL-17::GFP expression in a wild-type L3 larva. The four P6.p descendants (P6p.xx, arrows) strongly accumulate EGL-17. (B) EGL-17::GFP expression in a ndk-1(-) mutant L3 larva. The expression intensity is much reduced compared with the wild type (the image was taken with a much longer exposure time than that used for the control, as indicated by the much brighter background of gut autofluorescence). In addition, one of the P6.p granddaughters (the yellow arrow) fails to accumulate EGL-17 in this specimen. (A,B) DIC images are on the left, the corresponding fluorescent images on the right. (C) Quantification of expression intensity of EGL-17::GFP in P6p.xx cells. n=20; for comparing levels of faint expression between wild type and ndk-1(-): P<0.001, unpaired Student’s t-test.
