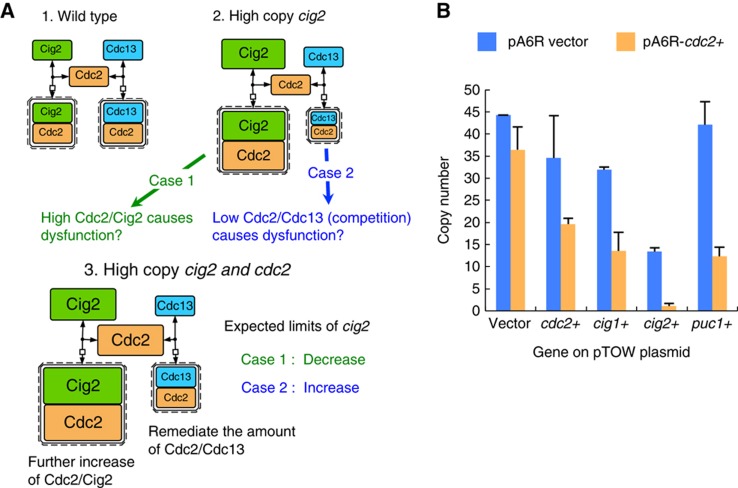
Figure 8.
2D-gTOW analysis to test the cyclin competition. (A) There are two possibilities determining the limits of cyclins. The case in cig2, as an example is shown. (1) In wild type, both Cig2 and Cdc13, and their Cdc2 complexes are balanced. (2) Upon high copy of cig2, there are two possible mechanisms to cause cell-cycle dysfunction. Case1: high Cdc2/Cig2 activity itself causes the dysfunction. Case2: Low Cdc2/Cdc13 activity due to the competition of cyclins for Cdc2 causes the dysfunction. (3) Both possibilities can be tested by the experiment increasing cig2 and cdc2 simultaneously, which situation leads to further increase of Cdc2/Cig2, as well as remediation of the amount of Cdc2/Cdc13. In this situation, the limit of cig2 should be increased if Case1 is true, and the limit of cig2 should be decreased if Case2 is true. (B) Testing cyclin competition. The copy number limit of each cyclin gene with increased cdc2 copy number (supplied by the pA6R plasmid) was measured. pTOWsp-M was used as the gTOW vector. The copy number for pTOW was measured in the leucine− condition.