Figure 2. Classical Model of p53 Activation.
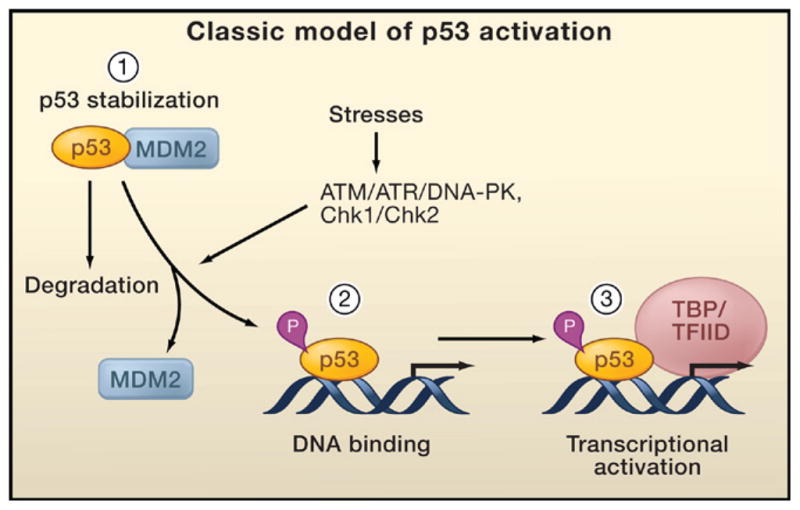
The classical model for p53 activation generally consists of three sequential activating steps: (1) stress-induced stabilization mediated by phosphorylation (P), (2) DNA binding, and (3) recruitment of the general transcriptional machinery. During normal homeostasis, p53 is degraded after Mdm2-mediated ubiquitination (left), while stress signal-induced p53 phosphorylation by ATM, ATR, and other kinases stabilizes p53 and promotes DNA binding. DNA-bound p53 then recruits the transcriptional machinery to activate transcription of p53 target genes.
