Fig. 3.
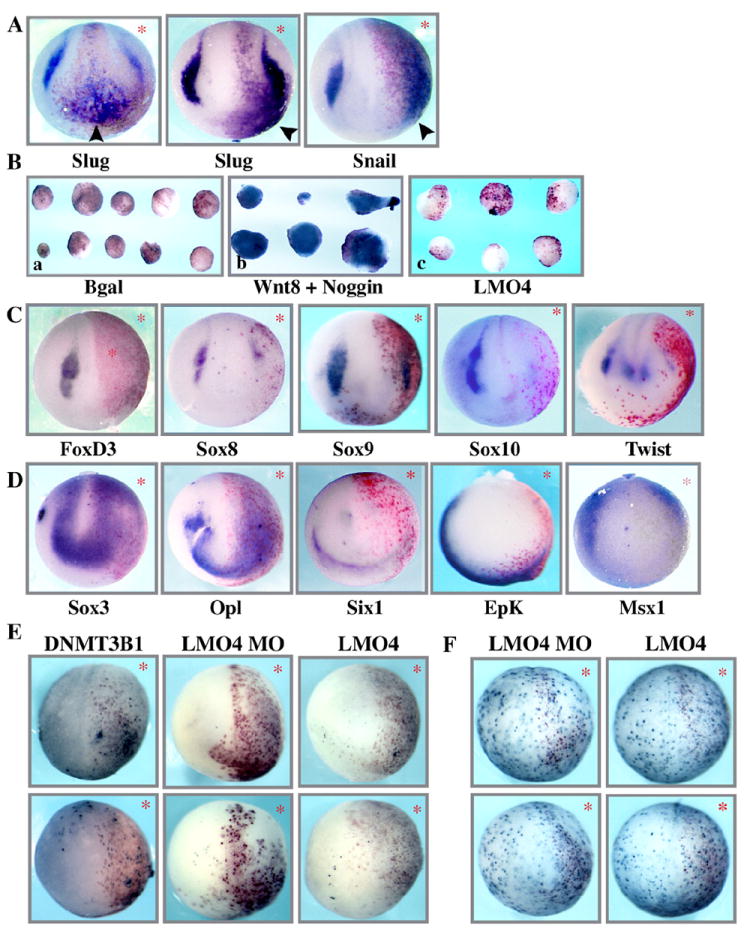
Excess LMO4 interferes with neural crest formation. (A) Whole mount in situ hybridization of embryos injected in one cell at two-cell stage with LMO4 and β-gal lineage tracer. Embryos were examined at mid-neurula stage (St. 17) with neural crest markers Slug and Snail, which display significant ectopic expression. B) Animal cap assay demonstrating that, in contrast to Wnt/noggin, LMO4 cannot induce Slug expression in isolated ectoderm. (C) Whole mount in situ hybridization of embryos injected in one cell at two-cell stage with mRNA encoding LMO4 and β-gal. Embryos were examined at mid-neurula stage (St. 17) with neural crest markers FoxD3, Sox8, Sox9, Sox10 and Twist expression of which, in contrast to Slug and Snail, were all inhibited by LMO4 misexpression. (D) In situ hybridization of stage 13 embryos injected with LMO4 and β-gal probed for neural plate marker Sox3, placodal markers Opl and Six1, epidermal marker Epk, and neural plate border markers Msx1 (St. 13). The expression of Slug and Snail is massively expanded while expression of other markers is inhibited. (E) TUNEL staining of stage 15 embryos injected with LMO4 MO, mRNA encoding LMO4, or apoptosis inducing factor DNMT3B1 (as a positive control). No significant changes in cell death were noted following either LMO4 up or down regulation. (F) phospho Histone H3 staining of stage 15 embryos injected with LMO4 MO or LMO4 mRNA. No significant changes in cell proliferation were noted following either LMO4 up or down regulation. * indicates injected side of embryo which is also marked by red gal staining.
