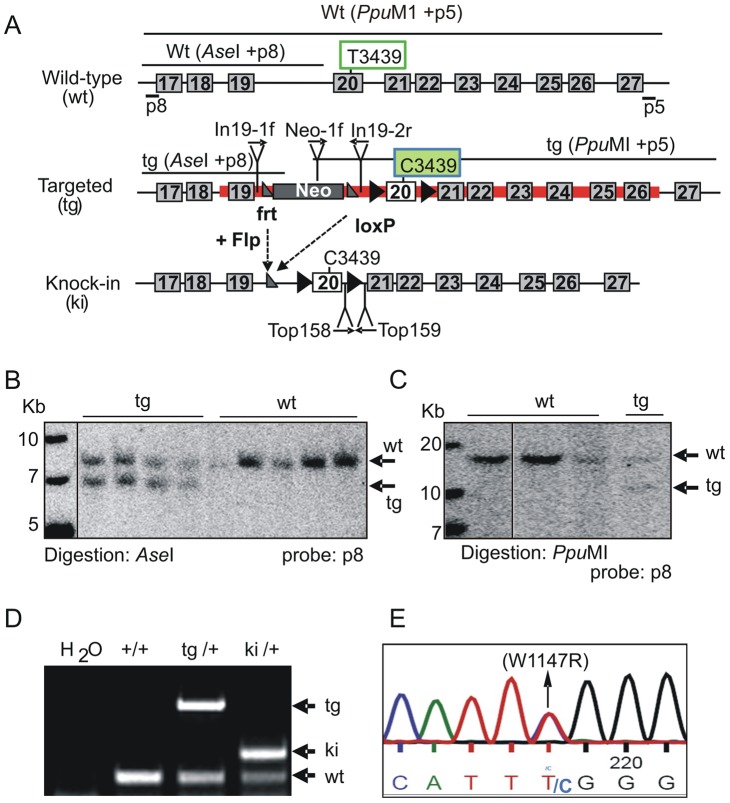
Figure 1. Generation of TopBP1 AAD mutant transgenic mice.
(A) Schematic of the C-terminus of the TopBP1 locus: wild type (wt), targeted (tg) and knock-in (ki) alleles. The red line marks the targeting vector. Exons are numbered in the boxes, Southern blot probes (p8 and p5), sizes of DNA fragments after indicated enzyme digestion and the location of primers for PCR genotyping are shown. The targeting vector contained a neomycin resistance gene (Neo) flanked by two frt sites (grey triangles). Exon 20 is flanked by two loxP sites (black triangle). Tryptophan 1147 (W1147) was mutated into arginine in AAD by replacing T3439 with C in exon 20. (B–C) Southern blot analyses of gene targeted ES cell clones: Homologous integration was verified by digestion with AseI and hybridization with a 5′ external probe (p8) and by PpuMI digestion and hybridization with a 3′ external probe (p5). (D) PCR genotyping analysis of the wild type, targeted and the knock-in allele following Neo excission. (E). Sequencing of genomic DNA from TopBP1ki/+ heterozygous MEFs confirms the mutation of TTT (tryptophan) to TTC (Arginine) (W1147R).