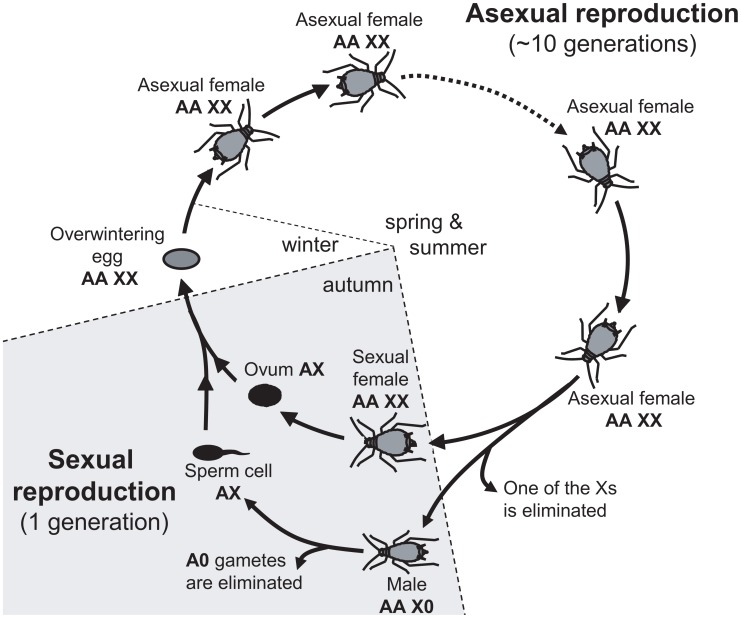
Figure 1. Annual life-cycle of the pea aphid and ploidy levels for autosomes (A) and sex-chromosome (X).
Overwintering egg, diploid for both types of chromosomes (AA and XX) gives birth to an asexual female. After several cycles of apomictic parthenogenesis, asexual females produce sexual females and males. Males inherit the same autosomal genome as asexual females, but receive only one of the female Xs: hence they are diploid for the autosomes and haploid for the X (represented as AAX0). Ovules (haploid for both the autosomes and the X) are generated by a normal meiosis, but males produce only X-bearing sperm (AX). The fusion of male and female gametes restores the diploid level at both the X and the autosomes.