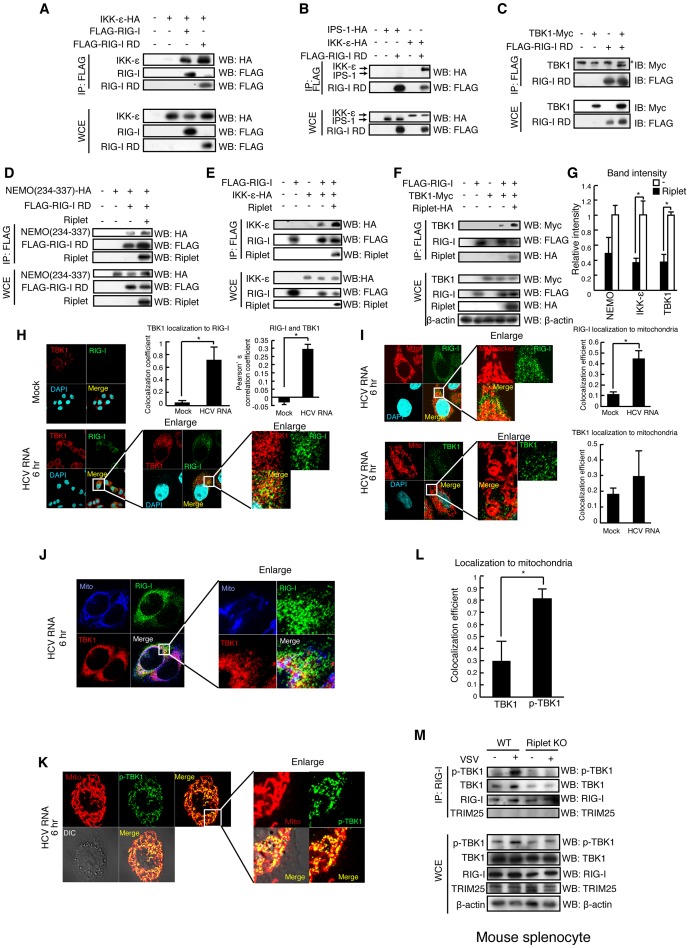
Figure 6. The association of TBK1 and IKK-ε protein kinases with RIG-I RD is enhanced by Riplet.
(A–F) The interaction of RIG-I with TBK1, IKK-ε, and NEMO was examined by immunoprecipitation assay. FLAG-tagged RIG-I or RIG-I RD expression vector was transfected into HEK293FT cells together with HA-tagged IKK-ε (A, B, and E), Myc-tagged TBK1 (C, F), HA-tagged NEMO ubiquitin binding region (D), and/or Riplet (D–F) expression vectors as indicated. 24 hours after the transfection, cell lysate was prepared, and immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-FLAG antibody. Asterisk indicates non-specific bands. (G) Relative band intensity of immunoprecipitated NEMO, IKK-ε, and TBK1 in D–F was determined. (H–L) Intracellular localization of endogenous RIG-I (H–J), TBK1 (H–J), phosphorylated-TBK1 (p-TBK1) (K), and mitochondria (I–K) were observed using anti-RIG-I (Alme-1), TBK1, p-TBK1 mAbs, and mitotracker. HeLa cells were stimulated with HCV dsRNA for six hours using lipofectamine 2000. Colocalization coefficient of TBK1 localization to RIG-I (H), RIG-I and TBK1 localization to mitochondria (I), and TBK1 and p-TBK1 localization to mitochondria (L) were determined (mean ± sd, n>10). Person's correlation coefficient of RIG-I and TBK1 was determined (H). (M) Splenocytes from wild type and Riplet KO mouse were infected with VSV at MOI = 10 for eight hours. Immunoprecipitation was performed using an anti-RIG-I rabbit monoclonal antibody (D14G6), and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Endogenous RIG-I, TBK1, TRIM25, and β-actin were detected using anti-RIG-I, p-TBK1, TRIM25, and β-actin antibodies.