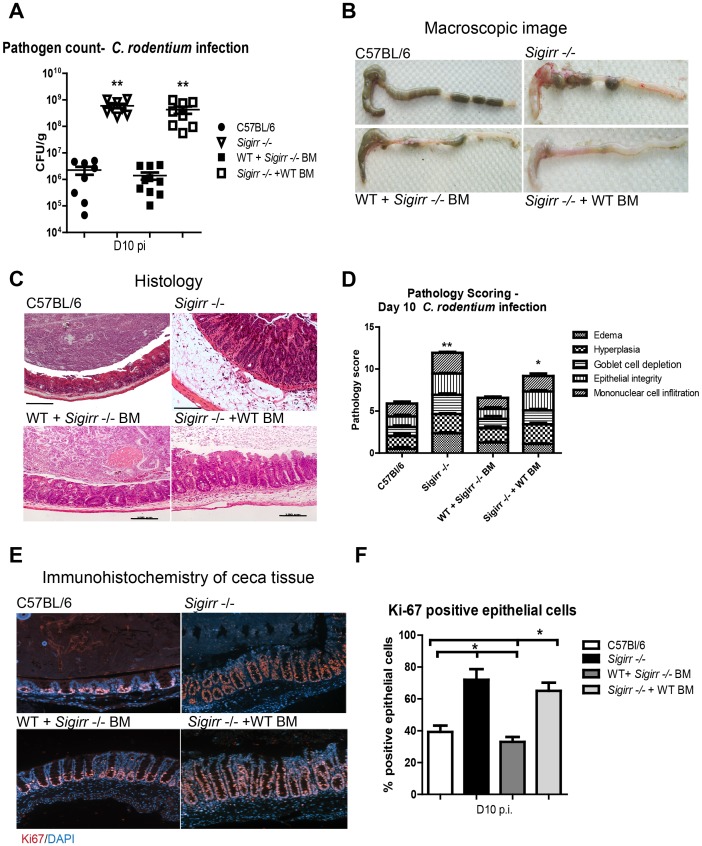
Figure 4. Non-BM derived cells mediate SIGIRR-dependent mucosal responses.
WT and Sigirr−/− mice were used to generate BM chimeric mice, which were then infected for 10 days with C. rodentium. Similar to Sigirr −/− mice, Sigirr −/− + WT BM mice displayed significantly heavier (A) pathogen burdens compared to WT mice. The ceca of Sigirr −/− + WT BM mice displayed (B) severe macroscopic and (C) histologic damage with significantly (D) greater pathology scores compared to WT and WT + Sigirr−/− BM mice. Sigirr −/− + WT BM mice exhibit higher levels of IEC proliferation as revealed by (E and F) Ki-67 staining. Pathogen counts represent mucosal associated bacteria. Results are pooled from 2 independent infections with n = 3–4 per group. Error bars = SEM, (Student t test (Figure A and D), One way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest for (Figure F), *P<0.05, **P<0.01). Images were taken at 200× magnification.