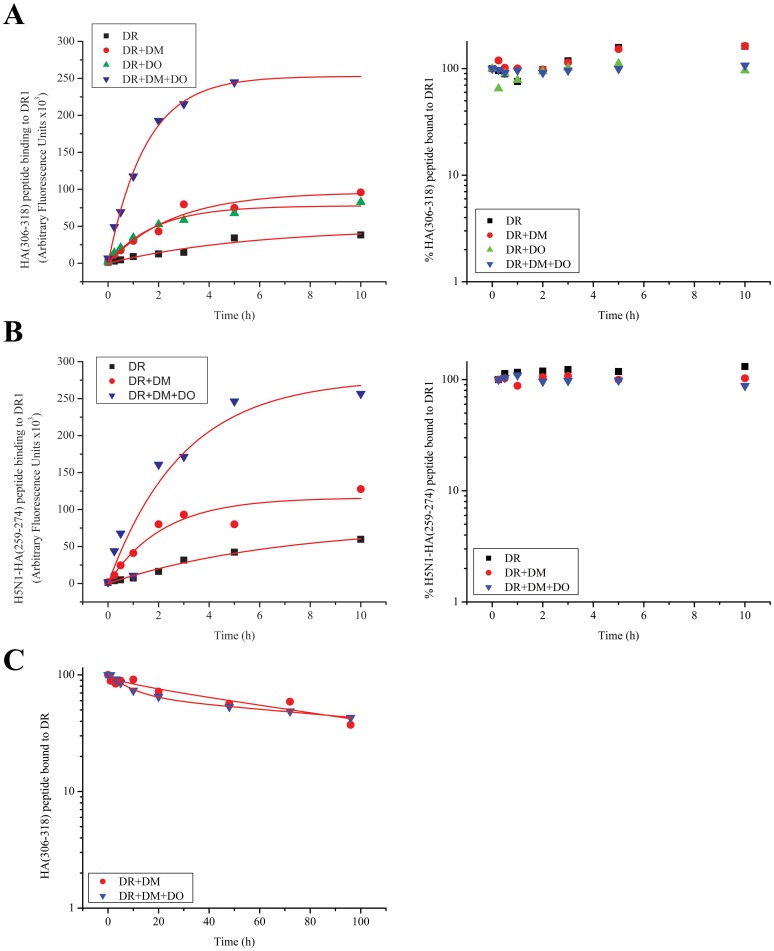
Figure 4. DO can increase the binding of peptides to DR1 molecules.
(A) Association (left) and dissociation (right) of HA(306–318) peptide to DR1 molecules with no accessory molecules (black squares), with DM (red dots), DO (green triangles) or both DO and DM (blue triangles) over the course of 10 hours. The fluorescence signals (Arbitrary Fluorescence Units) associated with the control samples incubated >10 hours in the absence of DR1 were measured: HA(306–318) peptide alone, 1390; HA(306–318)+DM, 1376; HA(306–318)+DO, 3316; HA(306–318)+DM+DO, 9236. (B) Association (left) and dissociation (right) of H5N1-HA1(259–274) flu peptide to DR1 molecules with no accessory molecules (black squares), with DM (red dots), DO (green triangles) or both DO and DM (blue triangles) over the course of 10 hours. The fluorescence signals (Arbitrary Fluorescence Units) associated with the control samples incubated >10 hours in the absence of DR1 were measured: H5N1-HA1(259–274) peptide alone, 1312; H5N1-HA1(259–274)+DM, 1250; H5N1-HA1(259–274)+DM+DO, 9012. (C) Prolonged 96 hour dissociation experiment of HA(306–318) peptide from DR1 molecules with DM (red dots) or both DO and DM (blue triangles). Data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.