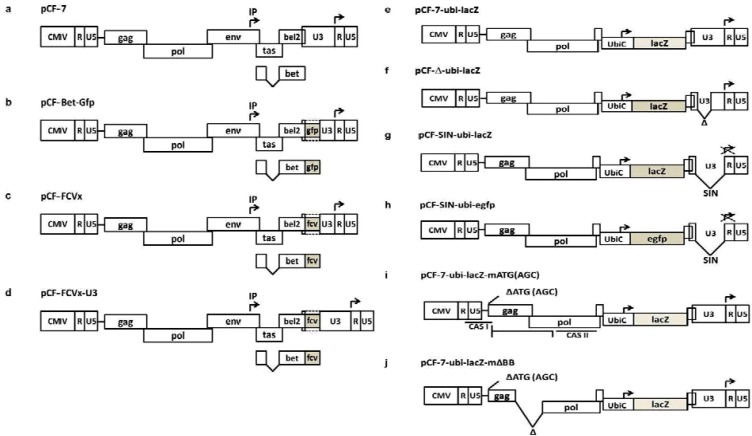
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of the different replication-components (RCs) (a–d, left panel) and replication-deficient (RD) (e–j, right panel) FFV vectors developed in the lab of the authors. FFV genes and long terminal repeats (LTRs) (U5, R, U3 regions) and heterologous genes are represented by boxes (not to scale). Broken arrows mark promoters and direction of transcription; inactivated promoters, by crosses; and deleted sequences and splice variants, as broken lines. (a) Authentic RC and CMV-IE promoter-driven FFV vector pCF-7 [22]. (b) Parental green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression vector pCF-Bet-Gfp. gfp is shown as a shaded box inserted into the deletion in the U3 region of the 3' LTR [22]. (c) Hybrid FFV-FCV clones (pCF-FCVx) carrying a deletion in the U3 of the 3' LTR. The FCV E inserts (E14, E23, and E24) are represented by shaded boxes [4]. (d) Chimeric FFV-FCV clones (pCF-FCVx-U3) with reconstructed U3. The different FCV E inserts (E14, E23, and E24) are represented by shaded boxes [4]. (e–g) The ubi-lacZ vectors, pCF‑7-ubi-lacZ, pCF-Δ-ubi-lacZ and pCF-SIN-ubi-lacZ, with the intact, truncated and functionally deleted Self-inactivating (SIN) LTR promoter and the ubi-lacZ cassette [30]. (h) pCF-SIN-ubi-egfp with egfp inserted into pCF-SIN-ubi-lacZ vectors by replacing lacZ [54]. (i–j) ubi-lacZ vectors pCF-7-ubi-lacZ-mATG (AGC) with mutagenesis of the gag ATG and pCF-7-ubi-lacZ-mΔBB with mutagenesis of the gag ATG and truncated gag-pol [54].