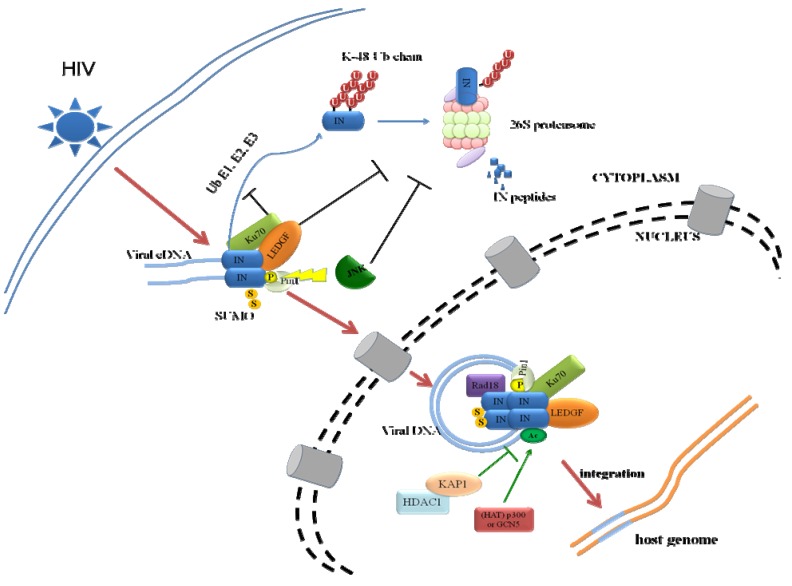
Figure 2.
Model for regulation of IN by various PTMs. The interactions of IN with LEDGF/p75, hRad18 and Ku70 prevent IN from K48-linked Ub proteasome degradation pathway. LEDGF/p75 prevents IN from degradation through the formation of IN‑LEDGF/p75 complex which stabilizes IN. Ku70 reduces total Ub level in the cell and specifically decreases Ub modification of IN through their protein-protein interaction. Protection of IN from proteasomal degradation by hRad18 is independent of its N-end rule, but its molecular mechanism involved is still unclear. Pin1 binds phosphorylated IN which is catalyzed by JNK, leading to conformational change and prolonged half-life of IN. Therefore, phosphorylation of IN antagonizes ubiquitination of IN. The fate of SUMOylated IN is currently unknown. Both phosphorylation and SUMOylation of IN seem to occur after reverse transcription but before integration. IN is acetylated by two HATs p300 and GCN5. Acetylation of IN enhances IN/DNA binding affinity and integration. KAP1 binds and deacetylates IN by recruiting HDAC1. For clarity, other cellular cofactors of IN and viral proteins have been omitted in the figure. Abbreviations: integrase (IN); post-translational modification (PTM); Lens Epithelium-derived Growth factor (LEDGF); human Rad18 (hRad18); Ubiquitin (Ub); c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK); histone acetyltransferase (HAT); histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1); small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO).