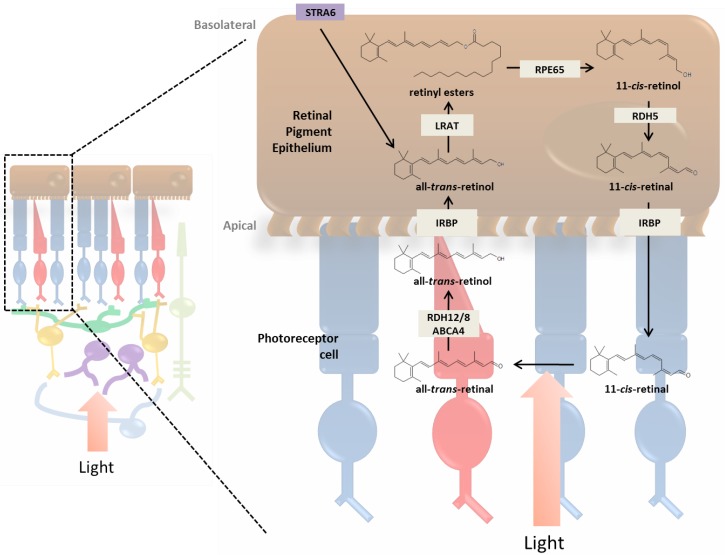
Figure 2.
Visual cycle. Absorption of light by visual pigments (rhodopsin or cone opsin) causes isomerization of 11-cis-retinal to all-trans-retinal, resulting in phototransduction. Decay of activated rhodopsin yields opsin and all-trans-retinal, which is released and pumped out into the cytosol by a photoreceptor specific ATP-binding transporter (ABCA4) and reduced to all-trans-retinol by all-trans-retinal dehydrogenases (RDH8 and RDH12). All-trans-retinol diffuses into the RPE where it is esterified by lecithin:retinol acyltransferase (LRAT) to all-trans-retinyl esters, which are stored in retinosomes. All-trans-retinyl esters are isomerized to 11-cis-retinol in a reaction involving a 65 kDa RPE-specific protein (RPE65). To complete the visual cycle, 11-cis-retinol is then oxidized by 11-cis–retinal specific RDH (RDH5) to 11-cis-retinal, which then diffuses back into the photoreceptor where it combines with opsin to regenerate visual pigments. IRBP, interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein; Stra6, stimulated by retinoic acid gene 6.