Figure 4.
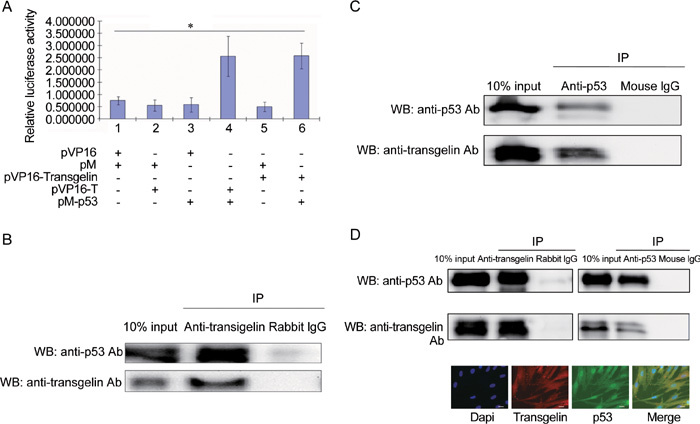
Interaction of transgelin with p53. (A): Mammalian two-hybrid assay. PC-3 cells cultured in 24-well plates were cotransfected with 0.5 μg pVP16, pM, pVP16-transgelin, pVP16-T and pM-p53 as indicated, together with 0.4 μg pG5-LUC reporter plasmid and 0.5 ng pRL-TK internal control plasmid. All values represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The luciferase activity of the interaction between pM-p53 and pVP16-T was set as positive control (lane 4) and that of the interaction between pM and pVP16 was set as negative control (lane 1). Interaction between pVP16-transgelin and pM-p53 was evaluated by measuring relative luciferase activity (*P < 0.01). (B): Ectopic transgelin coimmunoprecipitated with p53. LNCaP cells were transfected with 4.0 μg pCDNA-transgelin, and harvested 24 h after transfection. A total of 2 μg anti-transgelin antibody or rabbit IgG was added to 500 μg of LNCaP cell lysate for 4 h at 4ºC to immunoprecipitate the transgelin and p53 complex. (C): p53 coimmunoprecipitated with ectopic transgelin. A total of 2 μg anti-p53 antibody or mouse IgG was added to 500 μg of LNCaP cell lysate for 4 h at 4ºC to immunoprecipitate transgelin and p53 complex. (D): Endogenous transgelin coimmunoprecipitated with p53. BJ cell lysate was incubated with anti-transgelin antibody or anti-p53 antibody to immunoprecipitate the transgelin and p53 complex, and rabbit IgG or mouse IgG was used as control, respectively. Immunofluorescence staining illustrated the localization of transgelin and p53 in BJ cells. Scale bars=20 μm. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot.
