Figure 1.
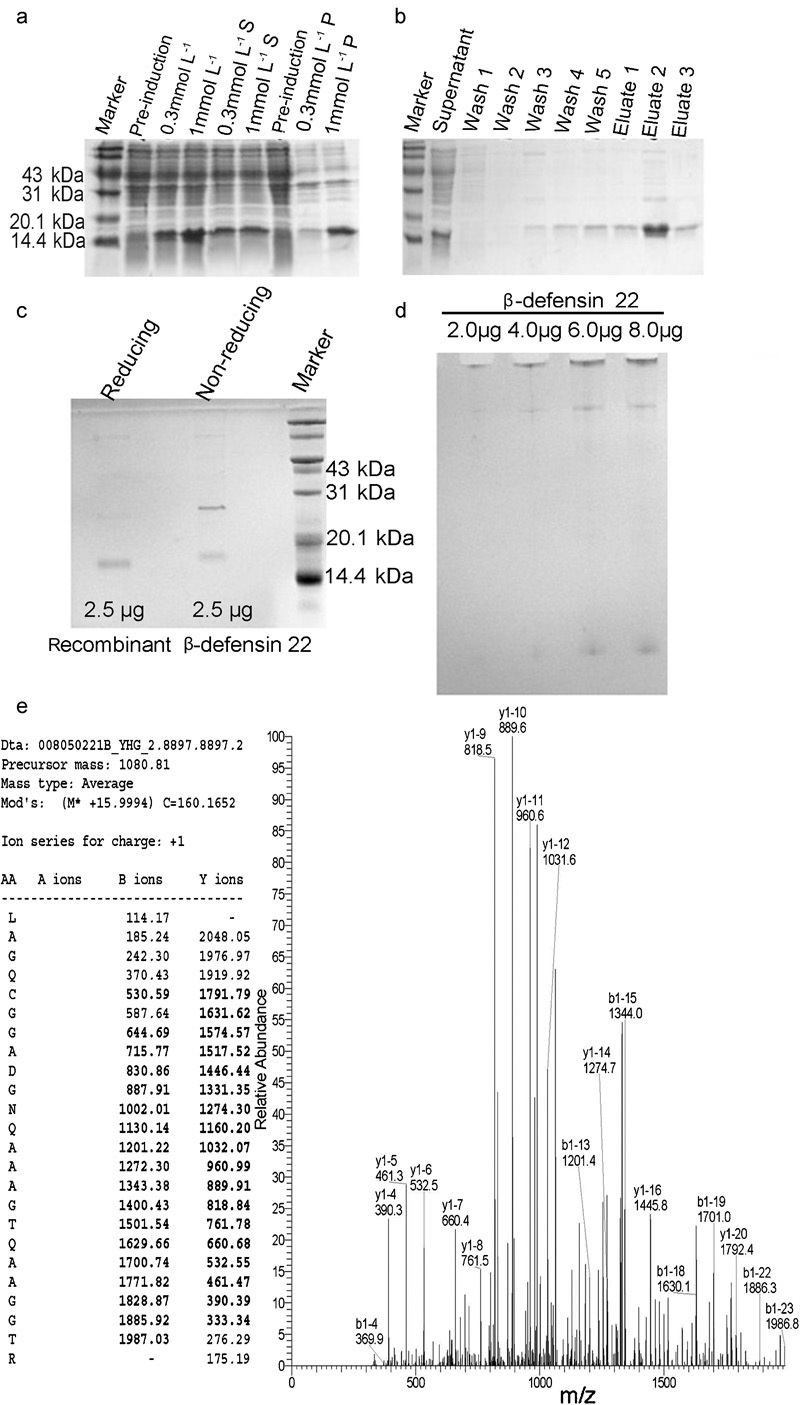
The recombinant expression (a), purification (b) and identification of rat recombinant β-defensin 22 (c–e). The cells before and after induction with varying concentrations of IPTG were analysed on 15% SDS–PAGE to optimize the expression conditions (a). ‘S' represents the supernatant of the cell lysate after centrifugation. ‘P' represents the pellet of cell lysate after centrifugation. The rat recombinant β-defensin 22 was purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography and analysed on 15% SDS–PAGE gels (b). ‘Wash 1–5' and ‘eluate 1–3' represents the collections of serial aliquots in the process of wash and elution. The purity of recombinant protein was then confirmed by 15% SDS–PAGE (c) and 16% acetic acid–urea–PAGE (d). ‘Reducing' and ‘non-reducing' represent recombinant β-defensin 22 treated with loading buffers containing and not containing 5% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol respectively. (e) Identification of the recombinant protein by LC-MS/MS analysis. A representative MS profile of an ion and its amino acid sequence were shown in (e). IPTG, isopropyl β-𝒹-1-thiogalactopyranoside; LC-MS/MS, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; Ni-NTA, nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid; SDS–PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
