Figure 1.
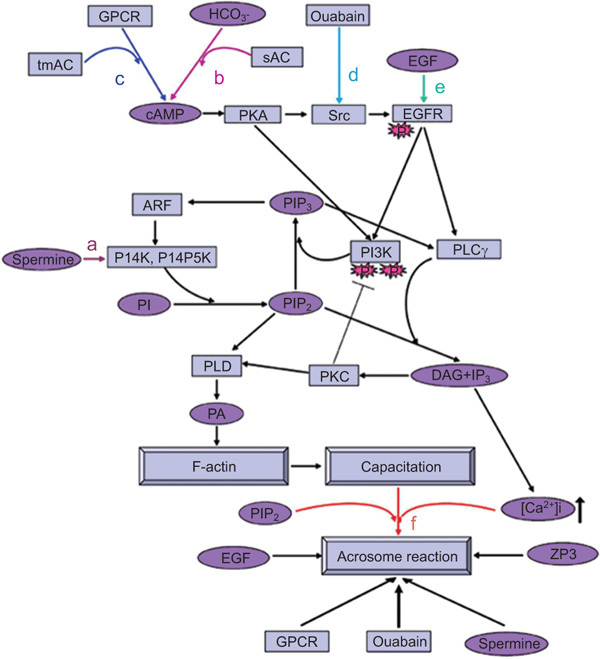
A model representing the mechanisms underlying EGFR activation during bovine sperm capacitation and AR. (a) Activation of PLD in sperm capacitation: at the beginning of the capacitation process, spermine can induce PI4K activation leading to PIP2(4,5) formation,19 a cofactor for PLD activation. The activation of PLD occurs by PKCα, which is already activated at the beginning of the capacitation.82 PLD can also be activated by activating PKA.27 Activation of PLD leads to F-actin formation during sperm capacitation.27 (b–e) Partial activation of EGFR in sperm capacitation: the EGFR can be activated via EGF (e) or by the cAMP-dependent PKA/Src system by activating GPCRs,9 which activate membrane-bound adenylyl cyclase to form cAMP, by HCO−3,7 which activates the soluble adenylyl cyclase (b, c), or by ouabain (d),10 which activates the tyrosine kinase Src. The activated EGFR can lead to PLD activation and F-actin formation via activation of PI3K/ARF/PI4K to form PIP2 and via PLC/PKC, two pathways needed for PLD activation. The activation of PI3K is upregulated by PKA and downregulated by PKC.82 Full activation of the EGFR before the acrosome reaction: further activation of the EGFR at the end of the capacitation process, by GPCR activation, ouabain, cAMP or EGF, enhances [Ca2+]i9 and PI3K activity, leading to F-actin breakdown and the occurrence of the AR (f). The addition of exogenous PIP2 or spermine, which leads to intracellular PIP2 formation (f), can induce the acrosome reaction via stimulating PIP2 hydrolysis to form IP3, leading to mobilization and increase in [Ca2+]i and activation of actin-severing proteins to depolymerize F-actin, resulting in the occurrence of the acrosome reaction (f). [Ca2+]i, intracellular Ca2+ concentration; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PI4K, phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase; PI4P5K, phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase; PIP2(4,5), phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C; PLD, phospholopase D; sAC, soluble adenylyl cyclase; tmAC, transmembrane adenylyl cyclase; ZP, zona pellucida.
