Figure 2. Cocaine, benzoylecgonine, and cocaethylene induce platelet–VWF string formation on the surface of stimulated HUVEC and BMVEC.
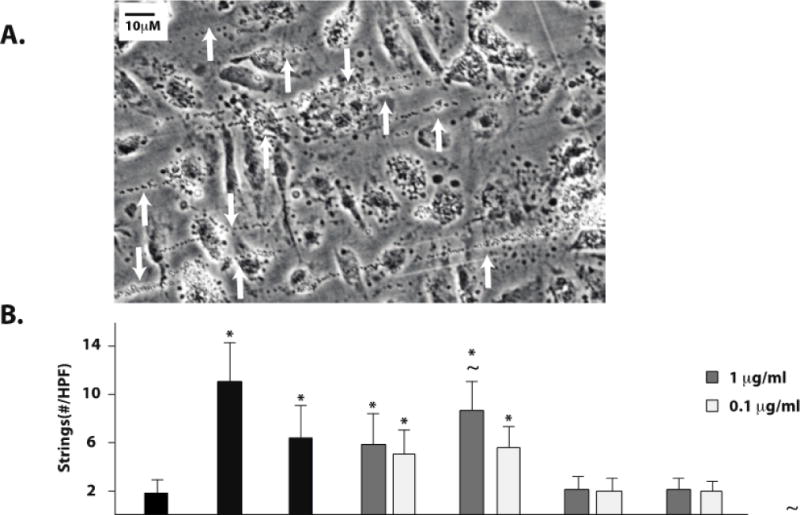
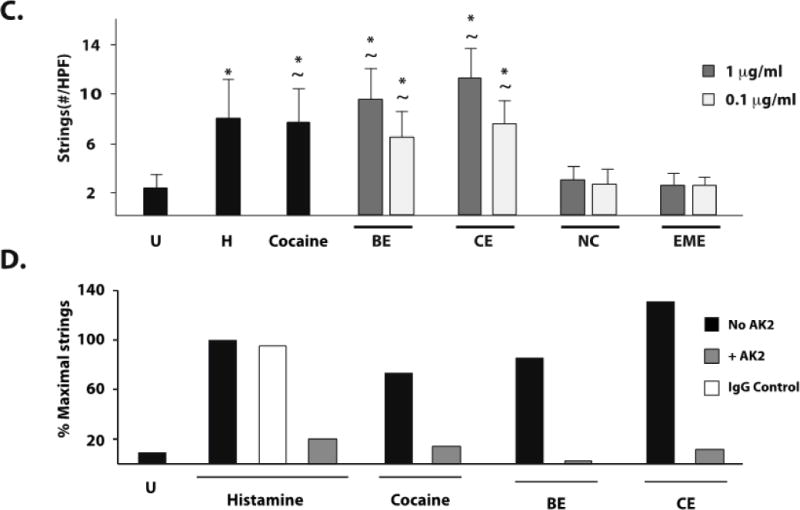
HUVEC or BMVEC were grown to confluence on glass coverslips and stimulated with histamine 50 μM (H), cocaine 1μg/ml, serum free media (untreated, U), or cocaine metabolites. The coverslips were then placed in a parallel-plate flow chamber and perfused with platelets at 2.5dyne/cm2. Platelet–VWF strings were visualized by phase-contrast videomicroscopy. Arrows indicate platelet-VWF strings. A) Video capture of platelet-VWF strings in a representative 40X field of histamine-stimulated HUVEC cells. Strings per 40X field were counted for HUVEC (B) and BMVEC (C). The results are expressed as means +/− SEM. * Tukey’s HSD test, as compared to untreated cells (p < 0.05). ~ Tukey’s HSD test, indicating no difference as compared to histamine treated cells (p > 0.05). D) GPIb dependence of string formation was assessed in the presence or absence of the GPIbα antibody AK2 after stimulation with no agonist (Untreated, U), cocaine, benzoylecgonine, or cocaethylene at 1μg/ml. The results are expressed as the percent maximal strings formed after histamine stimulation from a representative experiment.
