Fig. 2.
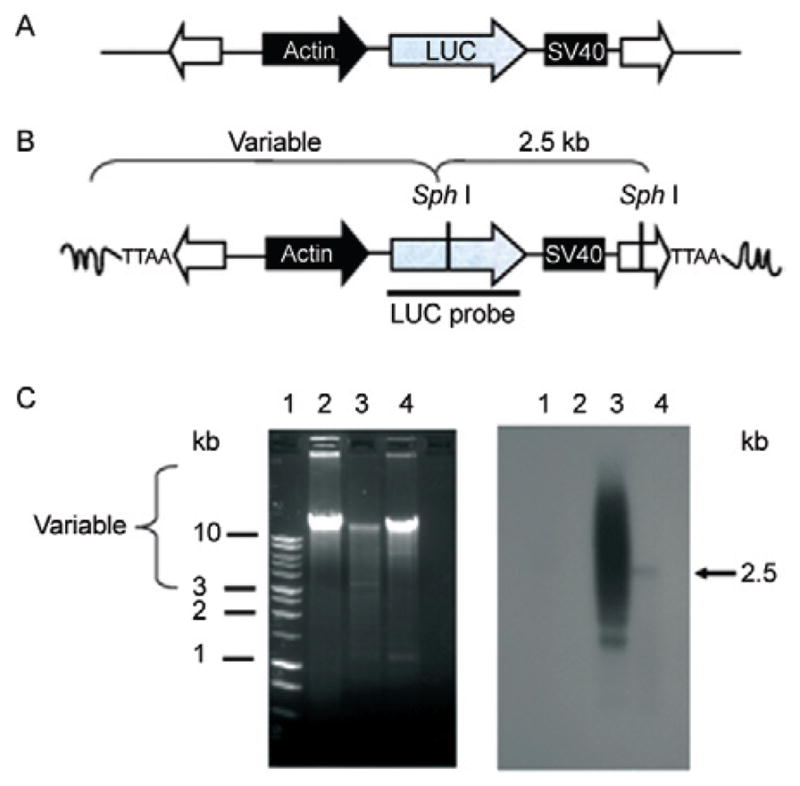
southern hybridization analysis of piggyBac transposon integration into schistosome chromosomes. A: representation of the (BssS 1)-linearized pXL-BacII-SmAct-Luc transposon construct. The transposon cassette included the firefly luciferase reporter (gray arrow) followed by the SV40 polyadenylation site (black box), driven by the schistosome actin gene promoter (black arrow) and flanked by the piggyBac terminal inverted repeats (white arrows); B: the structure of a piggyBac-mediated integration site, depicting variable length fragments expected following Sph I digestion of gDNA from piggyBac-transformed schistosomules. The luciferase probe (LUC) is indicated by a black bar; C: ethidium-stained gel of gDNA from Schistosoma mansoni digested with Sph I (left), southern hybridization of Sph I digested DNA (gDNA) to the labeled LUC probe (right), size standards in kilobases (kb) (Lane 1), gDNA from control schistosomes (Lane 2), gDNA from schistosomules after electroporation with donor piggyBac plasmid plus in vitro-transcribed transposase mRNA (Lane 3), gDNA from schistosomules seven days after electroporation with donor piggyBac plasmid alone (Lane 4). [From Morales et al. (2007), with permission].
