Figure 5. The RLCK genes RIPK-PIX8 and PBL2 are required for xopAC-mediated avirulence of Xcc strain 8004.
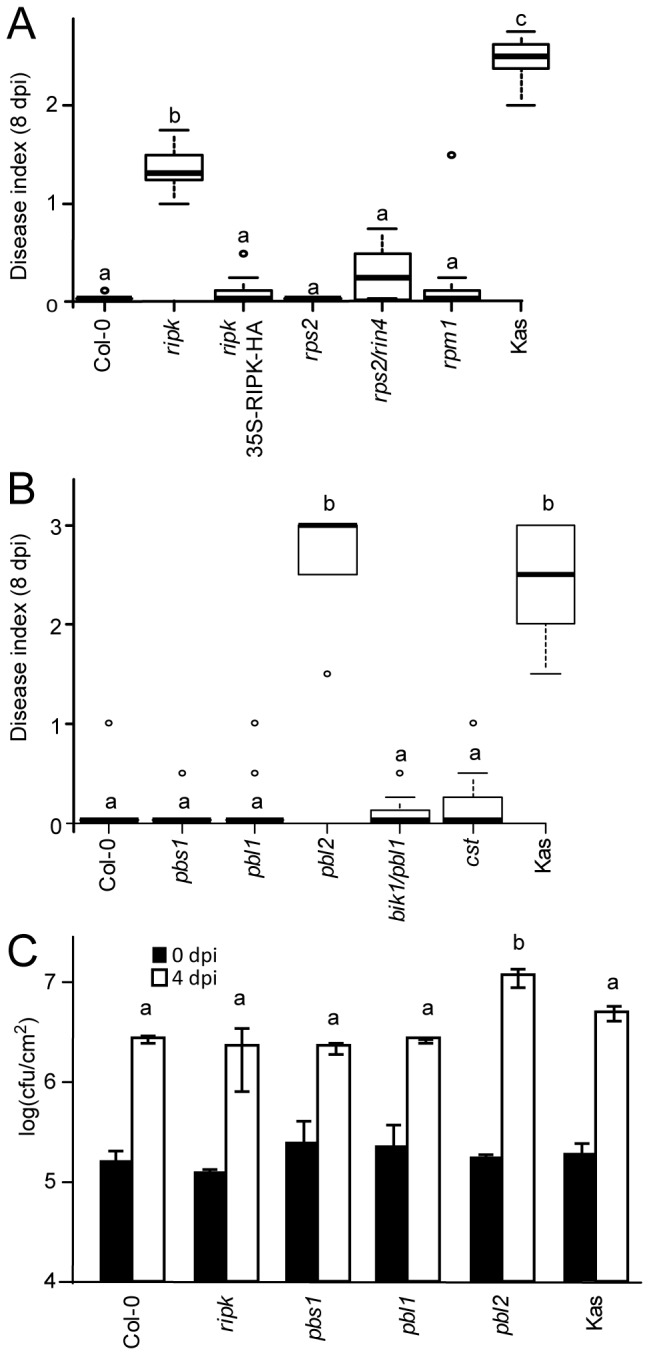
(A,B) Boxplot representation of pathogenicity of strain 8004 on Col-0 mutants and transgenics inoculated by piercing the central vein of the leaves is shown: middle bar = median; box limit = upper and lower quartile; extremes = Min and Max values. Kas was used as a susceptible control. Mutants in genes coding for the RIPK-RIN4/RPM1 complex (A) and various RLCK (B) were tested. Disease indices were scored 8 days post-inoculation: 0-1 no symptoms; 1-2 weak chlorosis, 2-3 strong chlorosis; 3-4 necrosis. N=3. Each time, at least 4 plants were inoculated on at least 3 leaves. Statistical groups were determined using a Tukey HSD test (P<0.001) and are indicated by different letters. (C) A bacterial suspension (105 cfu/ml) of Xcc strain 8004 was inoculated by piercing leaves of Col-0 mutants and transgenics. In planta bacterial populations in the inoculated areas were determined 0 and 4 days post-inoculation and expressed as log of colony-forming units per square cm (cfu/cm2). Standard deviations were calculated on two independent experiments. For each experiment, three samples of two leaf discs from different plants were collected for each strain. Statistical groups identified using a Wilcoxon test (P<0.05) are indicated by different letters.
