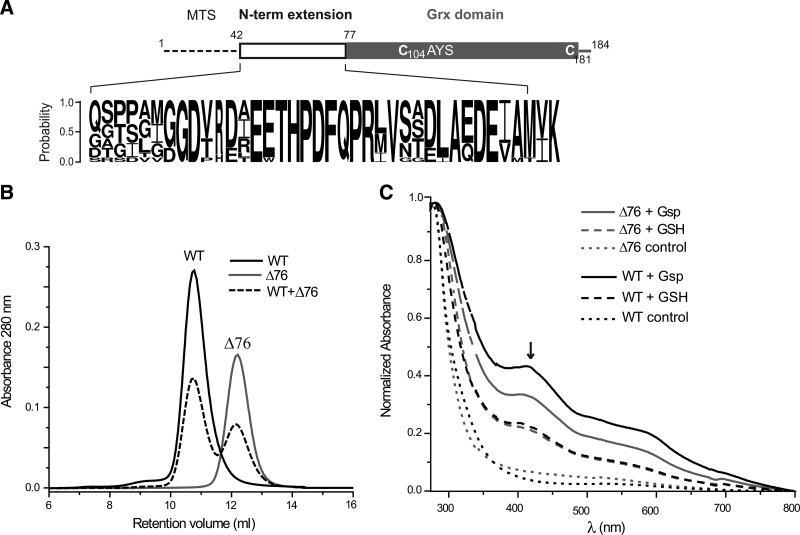
FIG. 1.
Structural organization, gel chromatography, and ISC formation of WT and Δ76 Tb1-C-Grx1. (A) Schematic representation of Tb1-C-Grx1 with the putative MTS, the N-terminal extension, and the Grx domain with the active-site CAYS (Cys104) as well as Cys181. The conservation in the N-terminal extension of 1-C-Grx1s from different trypanosomatids is shown as logo (see Supplementary Fig. S1 for details). (B) SEC of mature (WT), truncated (Δ76), and a mixture of both proteins. (C) UV–visible spectra of ISC reconstitution mixtures for 50 μM WT (black lines) and Δ76 (gray lines) Tb1-C-Grx1 in the presence of 150 μM GSH (dashed) or Gsp (solid). The cysteine desulfurase was omitted in control reactions (dotted lines). The spectra were normalized for the absorbance at 280 nm. The black arrow indicates the characteristic absorbance at 420 nm of the holocomplex. 1-C-Grx, monothiol glutaredoxin; Grx, glutaredoxin; GSH, glutathione; Gsp, glutathionylspermidine; ISC, iron–sulfur cluster; SEC, size-exclusion chromatography; WT, wild type; Tb, Trypanosoma brucei; MTS, mitochondrial targeting sequence.