Fig. 1.
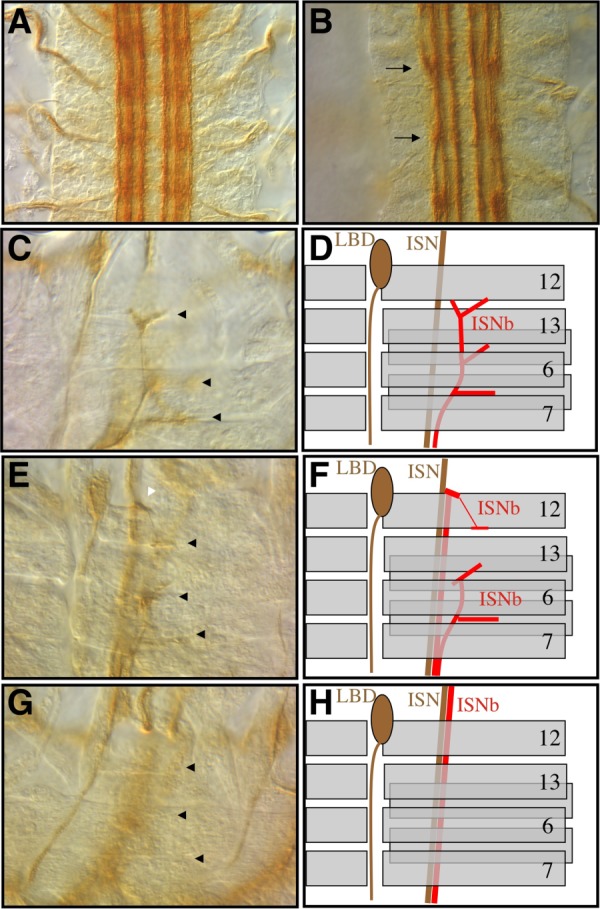
The misexpression phenotype of EP2056 and ME722 as seen in late stage-16 mAb 1D4-stained, dissected embryos. Embryos possess one copy of the Gal4 chromosome and one copy of EP2056 or ME722. A,B: Anterior is up and VNC longitudinal pathways are visualized. C–H: Anterior is left, dorsal is up, and the innervation of the ventral muscle domain by ISNb is visualized. A: A control embryo misexpressing an EP element with elav-Gal4, 24B-Gal4 that produces no phenotype. B: An EP2056 embryo upon misexpression with elav-Gal4, 24B-Gal4. Arrows point to deviation points of the lateral fascicle to the medial fascicle. C, E, G: Black arrowheads point to the three main innervation points of ISNb with the ventral muscles. C: The ME722 element with 24B-Gal4 showing the wild-type innervation for ISNb. E: The ME722 element with elav-Gal4 embryo showing an ISNb partial bypass phenotype. The white arrowhead points to the abnormal projection of a neuron off of ISN to innervate the cleft between muscle 12 and muscle 13. G: The ME722 element with elav-Gal4 embryo showing a full bypass ISNb phenotype with no innervation at any of the three normal ISNb innervation points. D, F, H: Schematic representations of the photomicrographs in C, E, and G showing the mAb 1D4-positive LBD neuron as well as the ISN and ISNb pathways. ISNb is shown in red and prominent ventral muscles are numbered.
