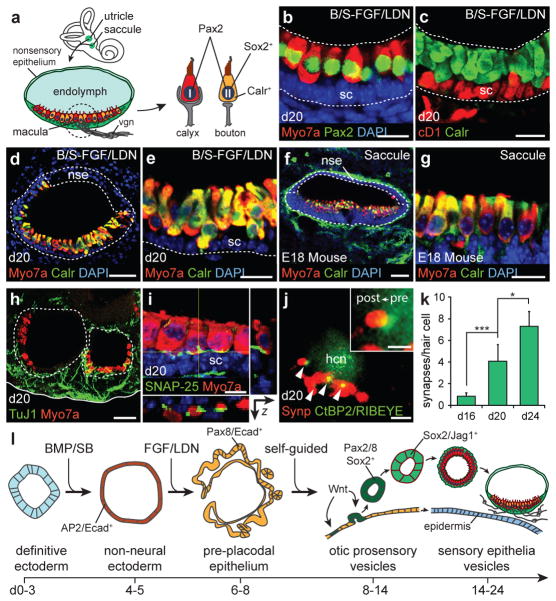
Figure 4. Stem cell-derived sensory epithelia are comparable to immature vestibular end organs.
a, Schematic of vestibular end organs and type I/II vestibular hair cells. vgn, vestibular ganglion neurons. b, Pax2 and (c) Calretinin is expressed in all Myo7a+ stem cell-derived hair cells on day 20. CyclinD1 (cD1) is expressed in supporting cells. d-g, The structural organization of vesicles with Calretinin/Myo7a+ hair cells mimics the E18 mouse saccule (sagittal view) in vivo. nse, non-sensory epithelium. h, TuJ1+ neurons extending processes to hair cells. i, The synaptic protein SNAP-25 is localized to the basal end of hair cells. j, The post-synaptic marker synaptophysin (Synp) co-localizes with CtBP2/RIBEYE (arrowheads and inset). hcn, hair cell nucleus. k, Quantification of synapses on day 16, 20 and 24 hair cells (n>100 cells, *P<0.05, ***P<0.001; mean ± s.d.). l, Overview of in vitro differentiation. Scale bars, 50 μm (d, f, h), 25 μm (b, c, e, g), 10 μm (i), 5 μm (j).