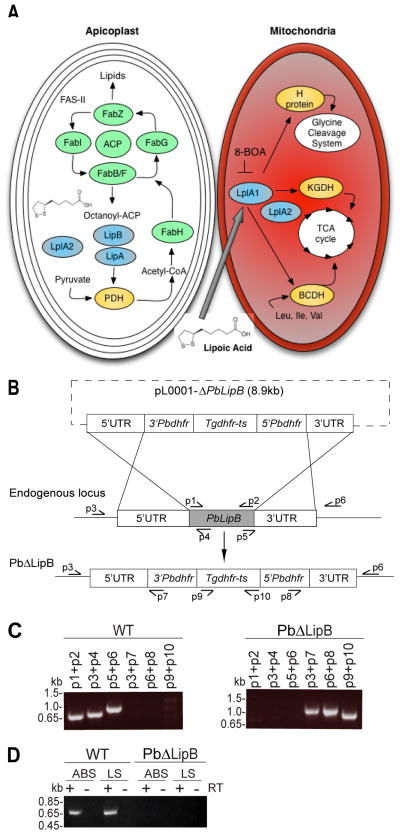
Fig. 1. Generation of PbΔLipB knockout parasites in Plasmodium berghei.
A. Schematic representation of lipoic acid synthesis and scavenging in the Plasmodium apicoplast and mitochondrion respectively. Enzymes responsible for the synthesis or attachment of lipoic acid to its target proteins are represented in blue. LipB and LipA synthesize lipoic acid from the octanoyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) precursor generated by the fatty acid biosynthesis type II (FAS-II) pathway. LipB is responsible for the attachment of octanoyl-ACP to the E-2 subunit of the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex within the apicoplast. LipA is responsible for creating the thiosulfur bonds. PDH converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, which primes the FAS-II pathway. In the mitochondria, LplA1 attaches scavenged lipoic acid to α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (KGDH) and branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase-E2 subunit (BCDH), which both feed into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, as well as the H-protein of the glycine cleavage system. Attachment of scavenged lipoic acid can be inhibited by the analog 8-BOA that targets the ligase LplA1. A second lipoate ligase, LplA2, has been localized to both the apicoplast and the mitochondria.
B. Schematic representation of the replacement strategy used to delete the PbLipB gene, based on homologous recombination and double crossover events between the pL0001-ΔPbLipB donor plasmid and the PbLipB genomic locus.
C. PCR confirmation of the PbLipB gene deletion and its replacement with Tgdhfr-ts. The left panel shows PCR products specific to the PbLipB coding sequence and its 5′ and 3′ UTRs in the parental P. berghei ANKA strain. This showed the expected band sizes of 0.70, 0.76 and 0.98 kb for p1+p2, p3+p4 and p5+p6 respectively. The right panel shows the replacement of PbLipB sequence with the Tgdhfr-ts marker in a PbΔLipB knockout clone. This shows the expected band sizes of 1.0, 0.98 and 0.93 kb for p3+p7, p6+p8 and p9+p10 respectively.
D. Reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR studies showing the loss of PbLipB transcription in PbΔLipB parasites and the expression of this gene in asexual blood stages (ABS) and liver stages (LS) in wild-type (WT) P. berghei ANKA parasites. + and − denote with and without RT. Reactions with the LipB-specific primers p1 + p2 showed the expected 0.7 kb transcription product in WT but not in KO parasites. Control reactions with P. berghei actin I-specific primers yielded the expected products with both KO and WT cDNA preparations (data not shown).