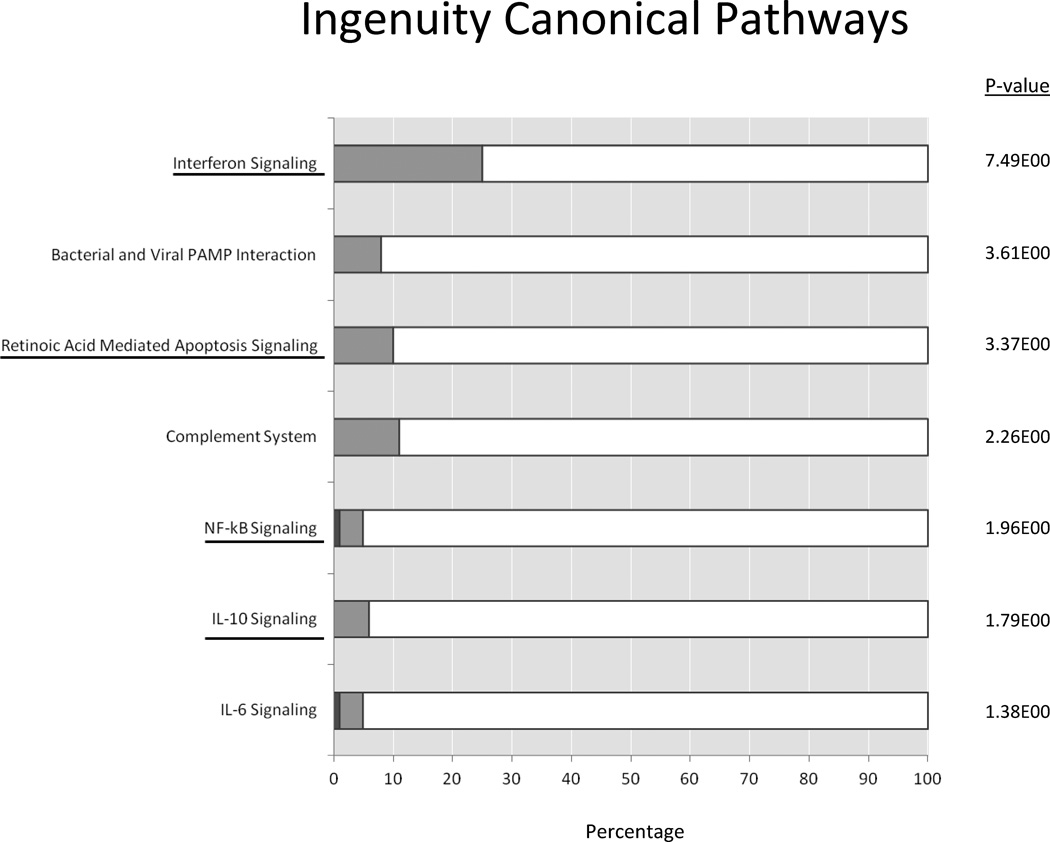
Figure 5.
Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) of PBMC RNAseq expression data. Shown are 7 pathways that belonged to groups of pathways identified by genomic convergence to be both genetically associated with IIT and significantly upregulated by IFNα in PBMCs. The percentage of genes that were upregulated are shown in light gray and genes that were downregulated are shown in dark gray, with the −log(p-value) shown at the right side of each bar. Interferon signaling pathway was found to be the most significantly upregulated. Other groups of pathways found to be associated with IIT and upregulated by IFNα in PBMCs included pattern recognition receptor related, apoptosis, complement, NFκB signaling, IL-10 signaling, and IL-6 signaling pathways. Four of these groups of pathways were found to be strongly associated with IIT in both datasets (all IIT cases vs. HCV controls and Caucasian IIT cases vs. healthy, Caucasian controls). These include interferon signaling, apoptosis related pathways, NFκB signaling, and IL-10 signaling (underlined).