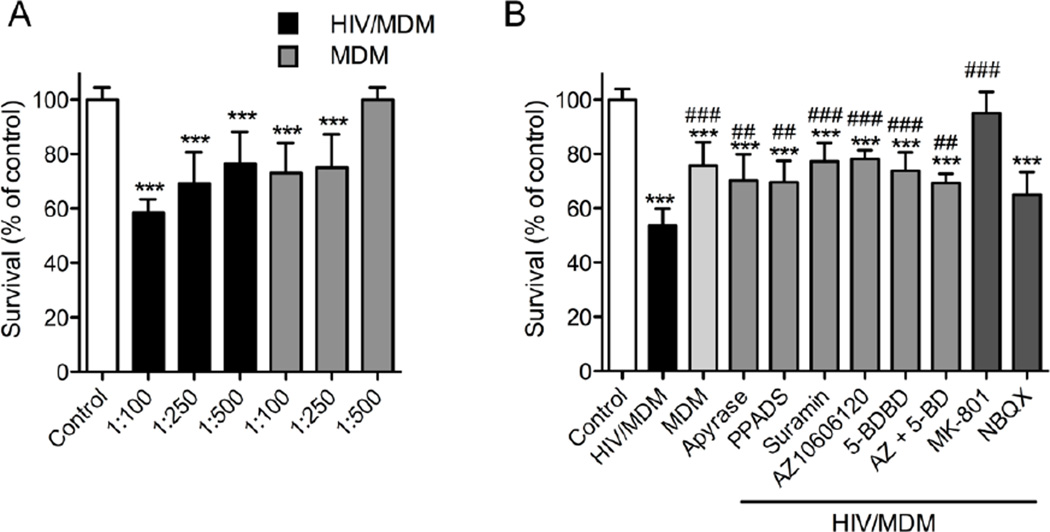
Figure 4. Calcium permeable purinergic receptors regulate HIV/MDM-evoked excitotoxicity.
Apoptotic nuclei with condensed or fragmented chromatin were determined by Hoechst 33342 DNA staining in neurons exposed to high-dose MDM or HIV/MDM supernatants (1:100 dilution) for 24 h. (A) Dose–dependent effect on neuronal survival upon exposure to MDM or HIV/MDM supernatants. (B) Neuronal apoptosis induced by HIV/MDM supernatants (1:100) was reduced by pre-treatment of HIV/MDM supernatant with apyrase (2 IU/10 µl HIV/MDM), and general antagonists of purinergic receptors (PPADS; 10 µM and Suramin; 100 µM), specific antagonists of P2X7 (AZ10606120; 10 µM), P2X4 (5-BDBD; 10 µM) and AMPA receptors (NBQX; 10 µM). Neuronal death was completely blocked by an antagonist to NMDA receptors (MK-801; 10 µM). Data are the average ± S.D. of 200 cells from three separate experiments per condition. ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc comparisons. *** = p < 0.001, ** = p < 0.01 compared with control, and ### = p < 0.001, ## = p < 0.01 compared with HIV/MDM supernatant.