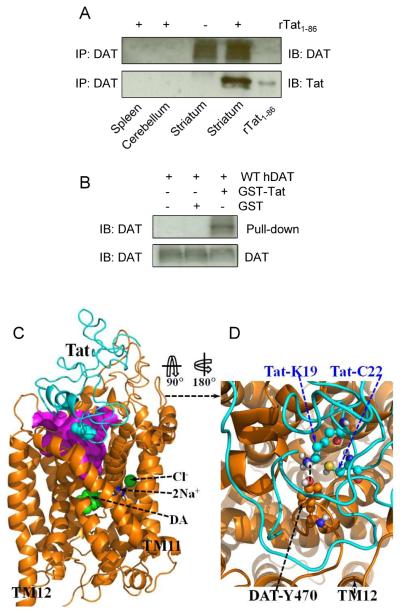
Figure 1.
A direct interaction between Tat and DAT and the energy-minimized hDAT(DA) binding complex following the MD simulation. Co-IP of DAT and Tat was performed by immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-DAT antibody as bait and immunoblot (IB) with anti-Tat antibody. (A) Co-IP of DAT and Tat. Rat synaptosomes from spleen, cerebellum, striatum were preincubated with (+, lanes 1, 2 and 4, from left) or without (−, lane 3) 350 nM recombinant Tat1-86 (rTat1-86). Top panel: DAT immunoreactivity was detected in striatum but not in spleen and cerebellum. Bottom panel: rTat1-86 bound to agarose beads was able to immunoprecipitate DAT in rat striatum but not in spleen and cerebellum. rTat1-86 (10 ng) was loaded in lane 5 as the positive control for Tat immunoreactivity. (B) GST-Tat1-86 bound to WT hDAT protein. Top panel: The GST-Tat1-86 fusion proteins were bound to glutathione-sepharose beads, and then incubated with cell lysates from CHO cells transfected with WT hDAT at room temperature for 1 h following Western Blot using anti-DAT. GST-Tat fusion protein bound to glutathione-sepharose was able to pull down DAT, but GST alone was not. Bottom panel: DAT immunoreactivity in CHO cells expressing hDAT was shown in all lanes. (C) Side view of the complex structure. Tat is shown as the ribbon in cyan color and hDAT(DA) as the ribbon in gold color. Atoms of residue C22 (Cys22) of Tat are shown as overlapped balls in cyan color. Atoms of substrate dopamine (DA) and the Cl− ion are shown as overlapped balls in green color. 2 Na+ ions are shown as balls in blue color. The vestibule (colored in purple) is represented as the molecular surface calculated by using the program HOLLOW (Ho and Gruswitz, 2008). (D) Local view of the anchoring residues Lys 19 (K19) and Cys22 (C22) of Tat inside the vestibule of hDAT(DA). Residues K19 and C22 of Tat are shown in ball-and-stick style, and colored by the atom types. Residue Tyr470 (Y470) of hDAT(DA) is also shown in ball-and-stick style and colored by the atom types. The hydrogen bonding between the K19 side chain of Tat and the hydroxyl oxygen atom on Y470 side chain of hDAT(DA) is indicated with the dashed line. Non-popar hydrogen atoms are not shown for clarity. The positions of transmembrane domain11 and 12 (TM11 and TM12) of hDAT(DA) are also labeled.