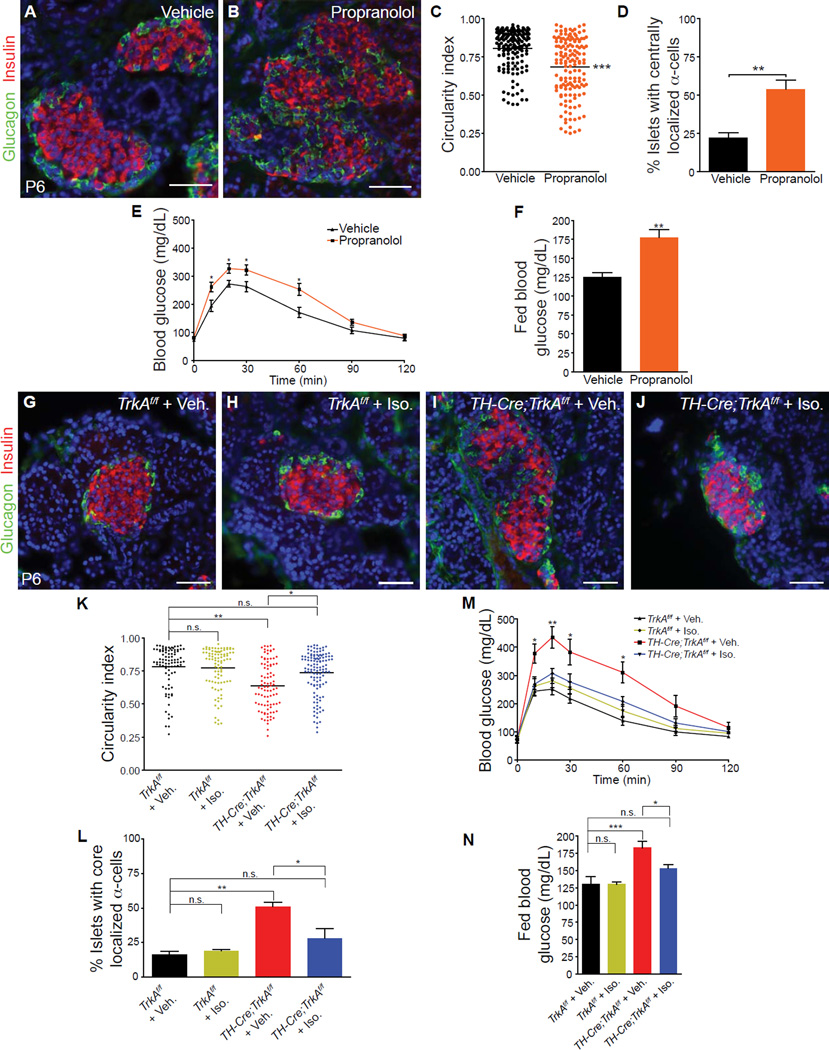
Figure 6. β-adrenergic signaling is necessary during development to regulate islet architecture and glucose metabolism.
(A,B) In vivo administration of propranolol (20 mg/kg body weight) during development (E18-P6) results in defects in islet architecture in neonatal (P6) mice, compared to saline-injected controls. (C,D) Quantification of islet shape and endocrine cell compartmentalization in mice injected with saline or propranolol. n=5 animals per genotype; mean ± SEM; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, t test. (E) Glucose intolerance in one month-old animals injected with propranolol during development (E18.5-P6), compared to vehicle-treated controls. n=7,9 mice for vehicle and propranolol respectively;, mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, t test. (F) Developmental administration of propranolol results in elevated fed blood glucose levels in mature animals at one month. n=7,9 mice for vehicle and propranolol respectively; mean ± SEM; **p < 0.01, t test. (G–L) Restoration of islet morphologies in neonatal TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice treated with a β-adrenergic receptor agonist, isoproterenol, from E18-P6. Isoproterenol administration (Iso, 30 mg/kg body weight) has no effect on islet architecture in control TrkAf/f mice (G,H), but normalizes islet structure and cytoarchitecture in TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice (J) compared to saline-injected TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice (I). (K,L) Quantification of islet shape and endocrine cell compartmentalization in TH-Cre;TrkAf/f and control mice injected with saline or isoproterenol. n = 3 mice for all treatments except for TH-Cre;TrkAf/f + Iso where n=4 mice; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p<0.01 one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. (M) Developmental administration of isoproterenol administration (E18-P6) rescues the glucose intolerance in one-month old TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice, compared to vehicle-injected TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice. Isoproterenol had no effect on glucose metabolism in control TrkAf/f mice. n=5 mice for vehicle- and Iso-injections in TrkAf/f mice; n=6 for vehicle-injected TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice and n=7 for Iso-injected TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p<0.01 as determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc test. (N) Normalization of fed blood glucose levels in in one-month old TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice treated with isoproterenol between E18-P6, compared to saline-treated TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice. n=5 mice for vehicle- and Iso-injections in TrkAf/f mice; n=6 for vehicle-injected TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice and n=7 for Iso-injected TH-Cre;TrkAf/f mice; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, ***p<0.001 one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test.